Eaton's Intelligent Power Manager (IPM) Vulnerability
Overview:
Eaton’s Intelligent Power Manager (IPM) software provides the tools needed to monitor and manage power devices in your physical or virtual environment keeping devices up and running during a power or environmental event. This software solution ensures system uptime and data integrity by enabling remote monitoring, managing and controlling devices on the network.
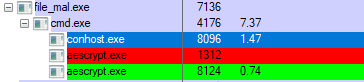
An arbitrary file deletion vulnerability has been reported in Eaton Intelligent Power Management and Eaton Intelligent Power Protector. The vulnerability is due to missing input validation in meta_driver_srv.js. A remote unauthenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a maliciously crafted packet. Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow attackers to delete arbitrary files on the target system.
The main program mc2 contains compressed Javascript code which is relevant for understanding this vulnerability. The web interface can be accessed over HTTP or HTTPS on ports 4679 and 4680, respectively.
CVE Reference:
Assigned the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) identifier CVE-2021-23279
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS):
The overall CVSS score is 8.7 (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:C/C:N/I:H/A:H/E:U/RL:O/RC:C).
Base score is 10.0 (AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:C/C:N/I:H/A:H), based on the following metrics:;
• Attack vector is network.
• Attack complexity is low.
• Privileges required is none.
• User interaction is none.
• Scope is changed.
• Impact of this vulnerability on data confidentiality is none.
• Impact of this vulnerability on data integrity is high.
• Impact of this vulnerability on data availability is high.
Temporal score is 8.7 (E:U/RL:O/RC:C), based on the following metrics:
• The exploit code maturity level of this vulnerability is unproven.
• The remediation level of this vulnerability is official fix.
• The report confidence level of this vulnerability is confirmed.
Technical Overview:
An arbitrary file deletion vulnerability exists in Eaton Intelligent Power Manager. The vulnerability is due to missing authentication check and missing input validation in the HTTP requests sent to “/server/ meta_driver_srv.js” endpoint. When a user sends a HTTP request to this endpoint, the code in meta_driver_srv.js will parse the JSON data in the data request parameter.
The code maintains the driverList list data structure in MetaDriverManager Javascript object that collects all driver IDs that are currently known to the application and can be found in the “configs/drivers/” directory. This directory maintains files where each file contains information about a driver ID and the file name is in the form of “X.drv”, where X is the driver ID.
After parsing the JSON data in the data request parameter, the code will then check if any driver ID in the driverList data structure is or is not present in the JSON data. If it is not present, the code will delete the file in the “configs/ drivers” directory where the file name matches the driver ID that was not present in the JSON data. The code makes a call to function deleteDriver() in the MetaDriverManager Javascript file to do the file deletion. Afterwards, it will add the data for each driver ID found in the JSON data that is not present in the driverList data structure. Namely, it will create the new “.drv” file in the “configs/drivers” directory with the provided JSON data in the request.
The problem with this code is the fact that it utilizes the driver ID keys in the provided JSON data to delete or create “.drv” file in the “configs/drivers” directory while not checking for directory traversal characters in the driver ID key. Therefore, the attacker can send the requests where the driver ID key in JSON data contains directory traversal characters.
*Note that the attacker will have to send two requests.
• In the first request, the attacker will send a malicious request containing driver ID that is a path to the file that is to be deleted. While processing this first request, the code will proceed to overwrite that file with the data provided in the data request parameter. However, the overwritten content would be in JSON format and not fully controlled by the attacker.
• The attacker then needs to send the second request where the driver ID, that was added when the first request was processed, is omitted from the request thereby initiating the code that will delete that file. By sending these two requests, the attacker can delete any file on the target system by employing directory traversal characters and the null character (%00). The null character is also needed to remove the trailing “.drv” extension from the maliciously crafted path.
Triggering the Problem:
• The target system must have the vulnerable product installed and running.
• The attacker must have network connectivity to the affected ports.
Triggering Conditions:
The attacker sends a malicious HTTP request to overwrite the contents of the file and then sends the second request to delete the same file. The vulnerability is triggered when the affected software processes the second request.
Attack Delivery:
The following application protocols can be used to deliver an attack that exploits this vulnerability:
• HTTP, over port 4679/TCP
• HTTPS, over port 4680/TCP
Attack Request:
Attack Response:
Patched Software:
Eaton has patched these security issues and new versions of the affected software are released. The latest versions can be downloaded from below location:
• Eaton IPM v1.69 – Download | IPM | Eaton
• Eaton IPP v1.68 – Download software | Power management | Eaton
SonicWall’s, (IPS) Intrusion Prevention System, provides protection against this threat:
• IPS: 15540 Eaton Intelligent Power Manager Arbitrary File Deletion
Vendor Advisory: