Spam campaign roundup: The Fathers Day Edition (June 13, 2014)
This Sunday is Father’s Day. It is that time of the year that we celebrate one of the most important persons in our lives. And as consumers are scrambling for last minute gift ideas and deals, cybercriminals are also increasing their efforts to divert advertising dollars into their hands.
Over the last week, the Dell SonicWALL threats research team has been tracking down all Father’s Day related spam emails.
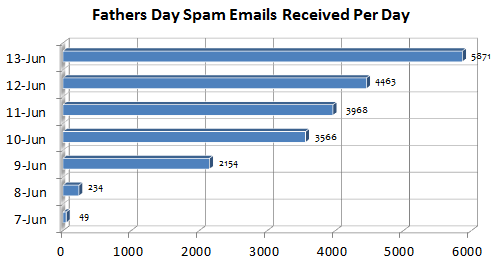
As Father’s Day weekend approaches, we are receiving an increasing amount of this holiday related spam emails. These emails have a common theme of trying to lure consumers to click on the links and provide their personal information in exchange for access to heavily discounted products or a chance to win gift cards and coupons. The following are some of the common email subjects:
- Print your coupon and Shop Amazon on US! Happy Father’s Day
- Save 81% on These 15 Premium Cigars + Humidor for Father’s Day!
- Shop for a luxury watch for Dad this Father’s Day.
- Robertcohen, Here’s a voucher for Lowe’s. Use for Father’s Day.
- Buy Dad Something Nice from Walmart- Father’s Day Coupon Enclosed

Most of these emails are purporting to come from popular department stores promising gift cards or coupons, that when clicked would take you to a URL different from the real merchant’s website. The consumer will then be asked to enter their personal information and to participate in a number of “offers” often costing money in fees or subscriptions without the guarantee of ever receiving the products and services or the free gift card at the end of the process.
The domain names used in the URLs embedded in the spam emails are just created in the past week and are all registered using a domain privacy service to keep the domain name owner’s personal information from showing up on global Whois lookups.

We urge our users to always be vigilant and cautious with any unsolicited email and to avoid providing any personal information, particularly if you are not certain of the source.
Dell SonicWALL Gateway Antivirus and Email Security service constantly monitor and provide protection against such malicious spam and phishing threats.