World Backup Day: Because Real Life Can Have Save Points Too
You’ve been playing for hours. You’ve faced two tough enemies in a row, and all signs indicate you’re about to take your remaining 12 hit points straight into a boss fight.
Up ahead a glowing stone beckons like a glimmering oasis.
“Would you like to save your progress?” a popup asks as you approach.
Um. YES!
But as obvious a choice as that seems, when the same opportunity presents itself in real life, a shocking number of people don’t take advantage of it.
What Do You Have to Lose?
The digital revolution has brought about unprecedented efficiency and convenience, ridding us of the need for bulky filing cabinets, media storage, photo albums, rolodexes and more. But every time we outsource the storage of our data to the cloud, we become a little more reliant on digital devices that are anything but infallible.
According to WorldBackupDay.com, more than 60 million computers worldwide will fail this year, and more than 200,000 smartphones—113 every minute—will be lost or stolen. But while the devices themselves are replaceable, their contents often aren’t. Imagine what could be at stake: All the photos you’ve taken of your children over the past two years. Every message you ever sent your spouse, all the way back to the very beginning. The last voicemail you ever got from your grandmother. All could disappear in an instant, even when associated with cloud accounts, as experienced below.
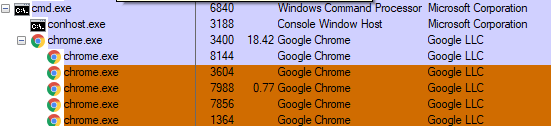
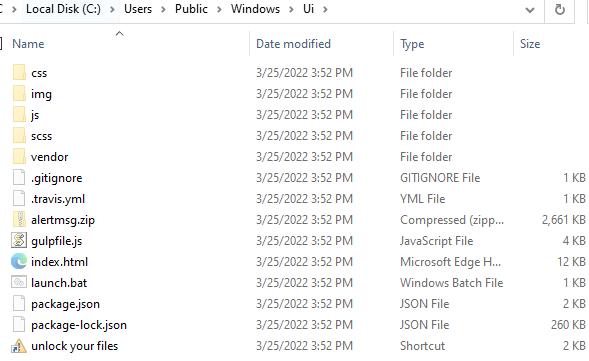
But the loss isn’t always just sentimental. Sometimes it’s professional too, as journalist Matt Honan found out in 2012. Honan used an iCloud account for his data, but had no backups — and when hackers gained access to the account, they remotely wiped his phone, tablet and computer. They also took over and deleted his Google account. “In the space of one hour,” Honan told Wired, “my entire digital life was destroyed.”
Good Backups Are Good Business
Businesses have fallen victim to devastating data loss, as well. In 1998, Pixar lost 90% of its film “Toy Story 2,” then in progress, due to the combination of a faulty command and insufficient backups.
And when social media/bookmarking site Ma.gnolia.com experienced a database failure resulting in the loss of all user data, it ultimately shuttered the company. “I made a huge mistake in how I set up my [backup] system,” founder Larry Halff said of the incident.
The Cultural Cost of Insufficient Backups
While World Backup Day’s primary goal is to encourage people to create and check their backups, it also aims to spark discussion of an enormous task: how to preserve our increasingly digital heritage and cultural works for future generations.
Due to insufficient archiving and backup practices, many cultural properties have already disappeared. For example, an entire season of the children’s TV show “Zodiac Island” was lost forever when a former employee at the show’s internet service provider deleted over 300GB of video files, resulting in a lawsuit over the ISP’s lack of backups.
And decades before, a similar fate befell the now-iconic sci-fi series “Dr. Who.” The Film Library of Britain and BBC Enterprises each believed the other party was responsible for archiving the material. As a result, the BBC destroyed its own copies at will, resulting in the master videotapes of the series’ first 253 episodes being recorded over or destroyed. Despite the existence of secondary recordings and showrunners obtaining copies from as far away as Nigeria, 97 episodes are still unaccounted for and presumed lost for good.
How to Ensure Your Digital Future Today
With so much at stake, you’d think almost everyone would back up their data at least occasionally. This isn’t the case, however. According to WorldBackupDay.com, only about 1 in 4 people are backing up their data regularly, and an astounding 21% have never made a backup.
This phenomenon is also seen at the corporate level. While 45% of companies have reported downtime from hardware failure and 28% reported a data loss event in the past 12 months, FEMA reports that 1 in 5 companies don’t have a disaster recovery/business continuity plan (and thus don’t typically have current backups.) With 20% of SMBs facing catastrophic data loss every five years, being left unprepared is much less an “if” than a “when.”
The difference in outcome for these businesses is stark. Ninety-three of businesses that experienced data loss and more than ten days of downtime filed for bankruptcy within a year. But 96% of businesses that had a disaster recovery plan fully recovered operations.
While a good backup plan will require ongoing attention, today is a great day to start — and even one backup is a tremendous improvement over no backups at all. The World Backup Day website is full of information on online backup services, external hard drive backup, computer backup, smartphone backup, creating a NAS backup, and other methods of preserving your data.
If you’re like many IT professionals and already understand the importance of backups, today’s a perfect day to test your backups out and make sure they’re still fully operational. It’s also a good opportunity to share the importance of backups with bosses, colleagues and friends.
After all, if you’re an individual, you won’t get an “extra life” to go back and relive all the memories you might lose if your device fails. And if you’re a small- or medium-sized business owner and lose all your data, having backups might be the difference between “Continue” and “Game Over.” On World Backup Day and every day, the choice is up to you.
To learn more about backups, visit WorldBackupDay.com.