The Sonicwall threat research team have recently observed a new variant of BitPyLock ransomware. This family of ransomware surfaced in early 2020. It encrypts files and also threatens extortion by claiming to have sent files to the attackers server. This claim, however, is not true. In addition to this, the decryption key can be easily obtained through basic reverse engineering.
Infection Cycle:
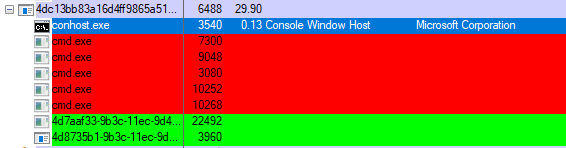
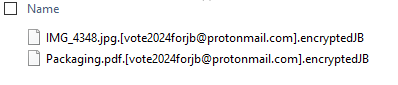
Upon infection, files on the system are encrypted. Unlike most ransomware, the filenames remain unchanged.
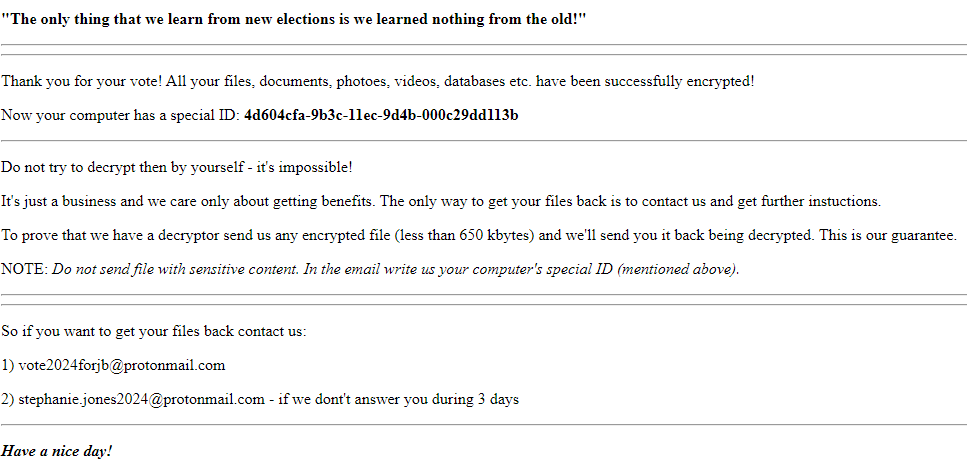
The following message is displayed on the desktop:
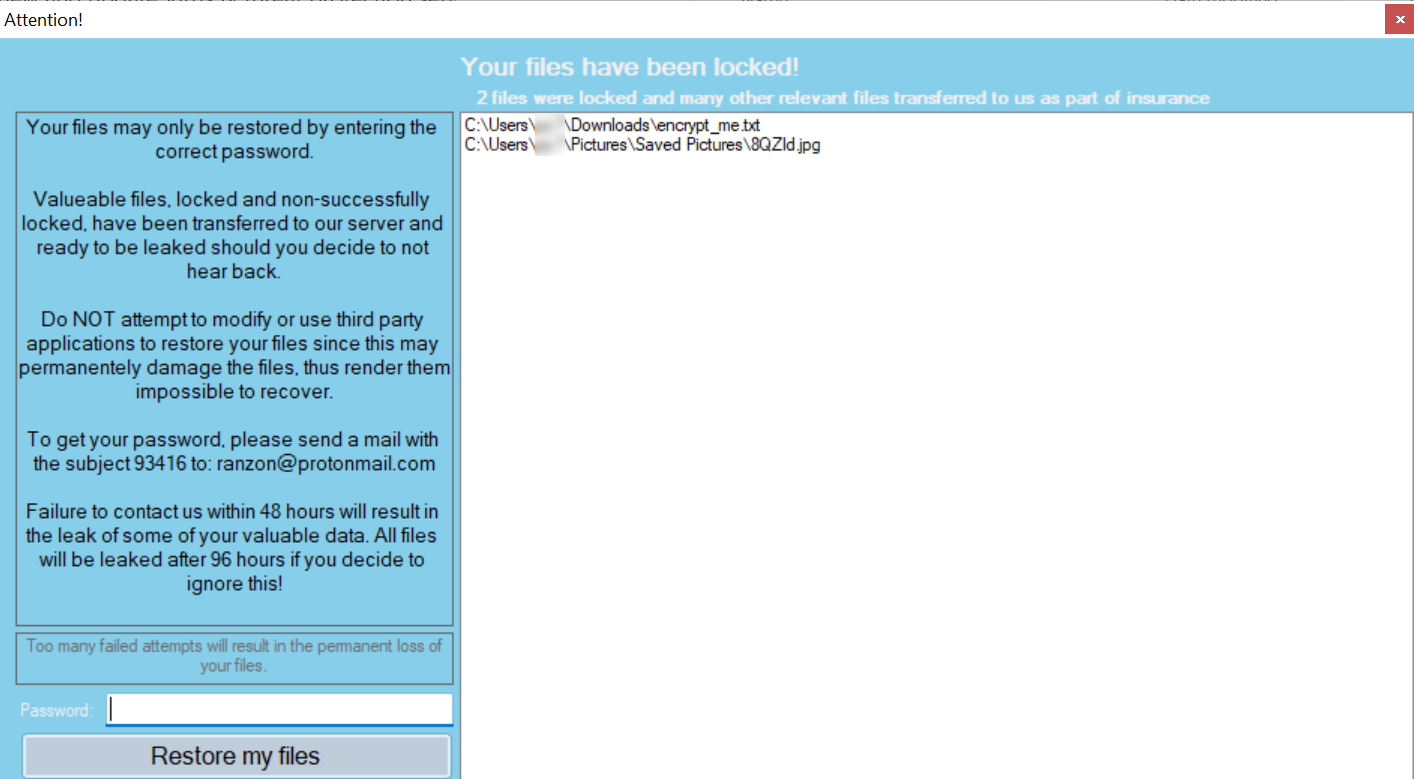
The note mentions that files have been transfered to the attackers server. However, this is not the case. There was no network traffic observed during the infection cycle.
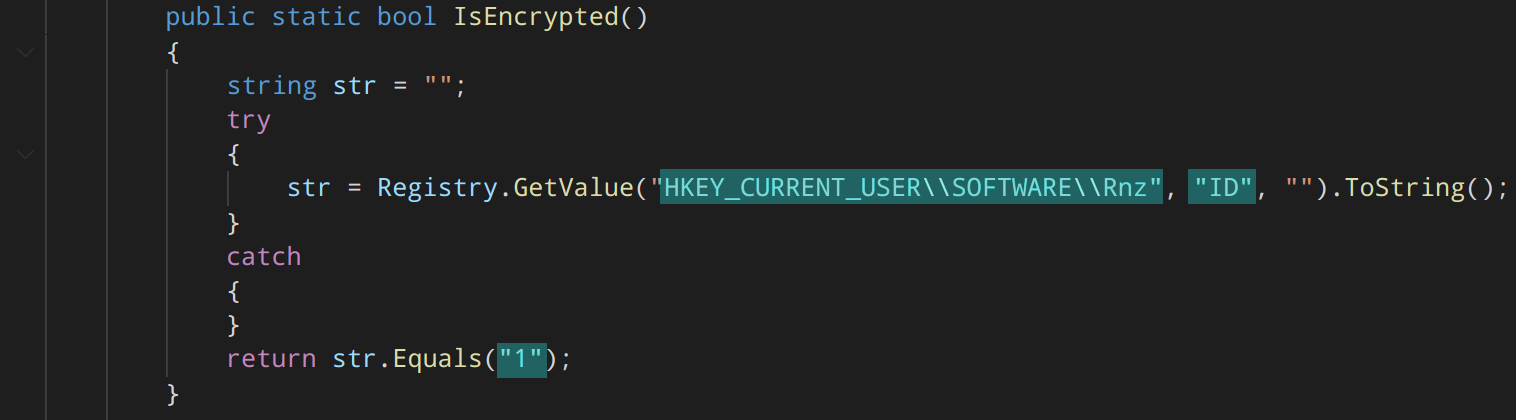
The following keys are added to the registry:
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Rnz ID “1”
- HKEY_USERS\S-1-5-21-4236731928-1562650142-1211730654-1001\Software\Rnz ID “1”
The following file is added to the filesystem:
- %APPDATA%\Roaming\rnz.bin
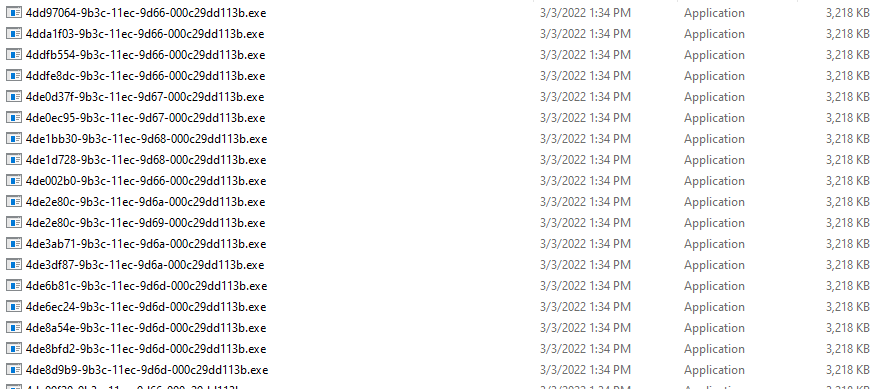
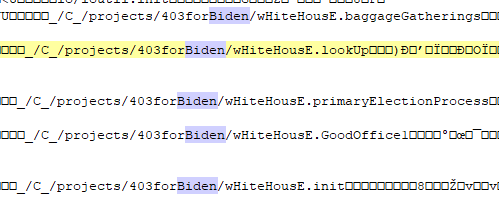
rnz.bin contains the following data (list of encrypted files):
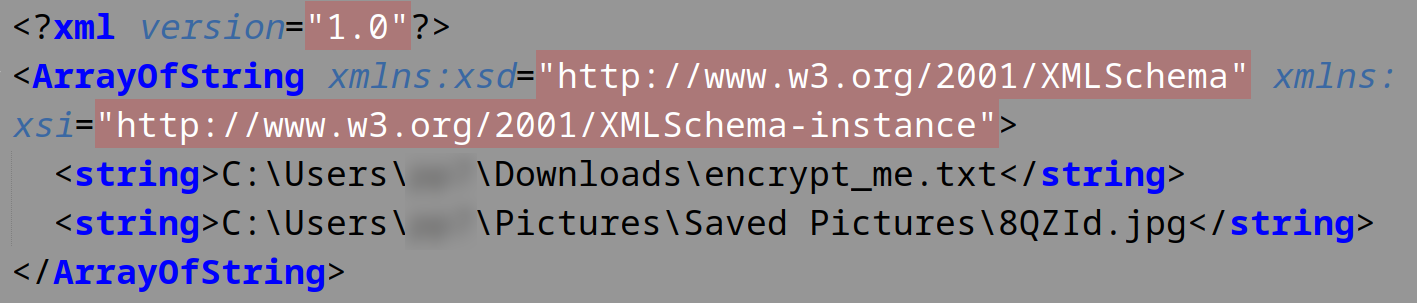
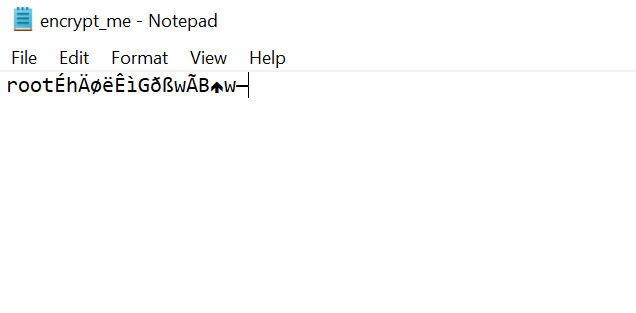
Each encrypted file has the string “root” prepended to its contents:
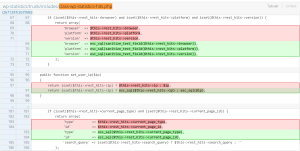
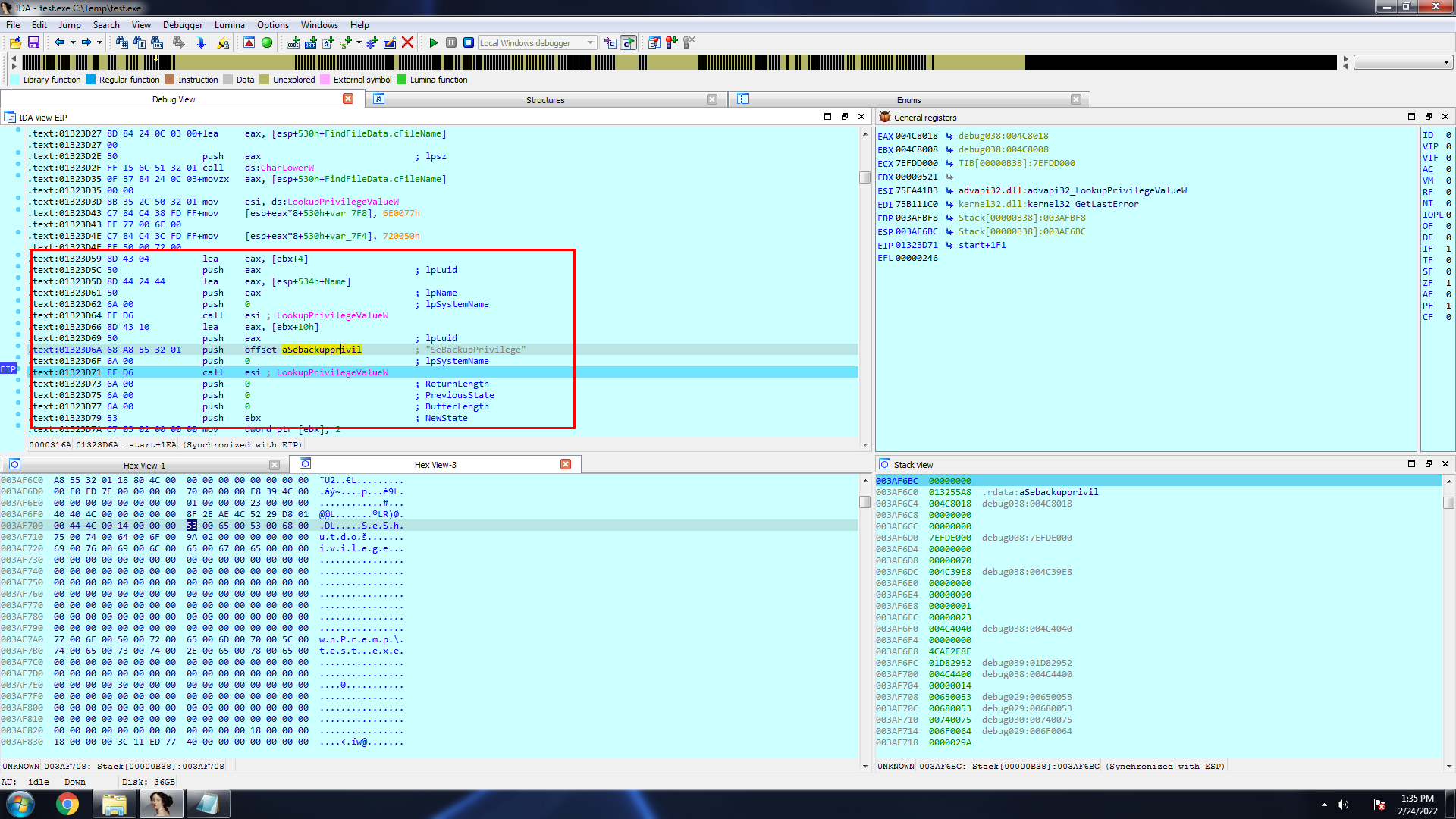
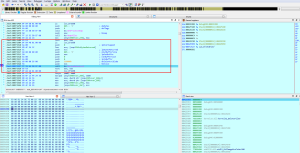
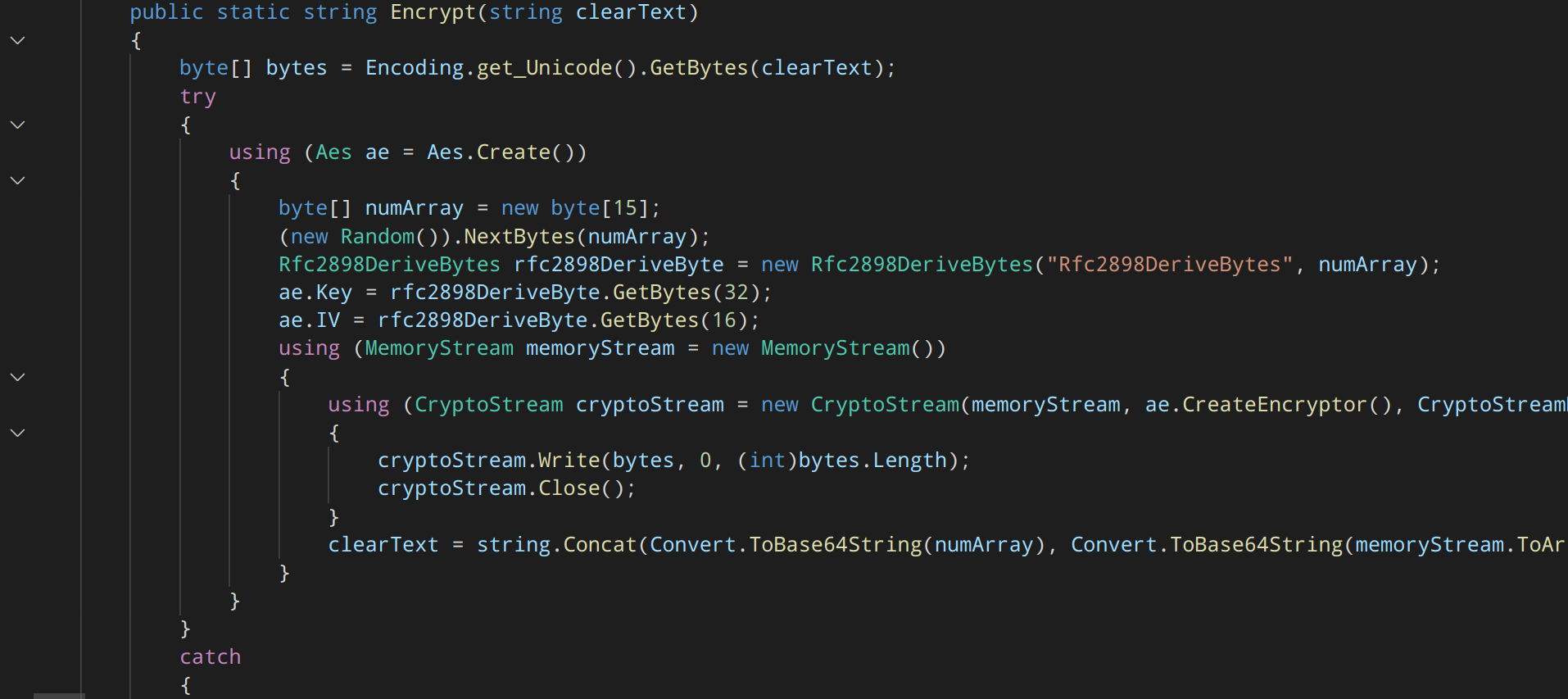
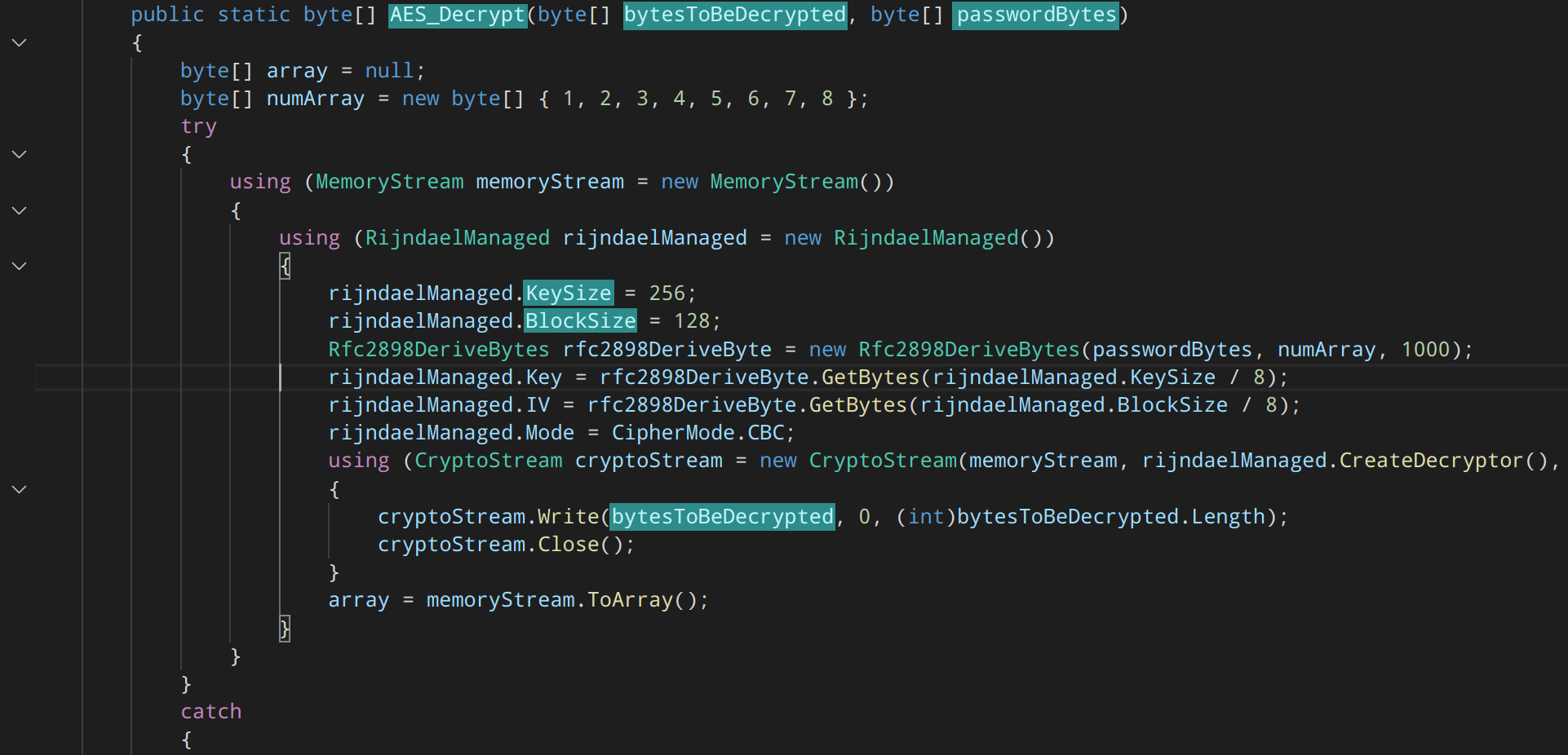
The malware is written in C# and is trivial to decompile. The encryption and decryption functions can be easily seen in the code:
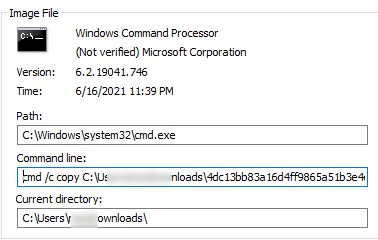
A registry key is added to mark infection:
The decryption key and file type targets can be clearly seen in the code:
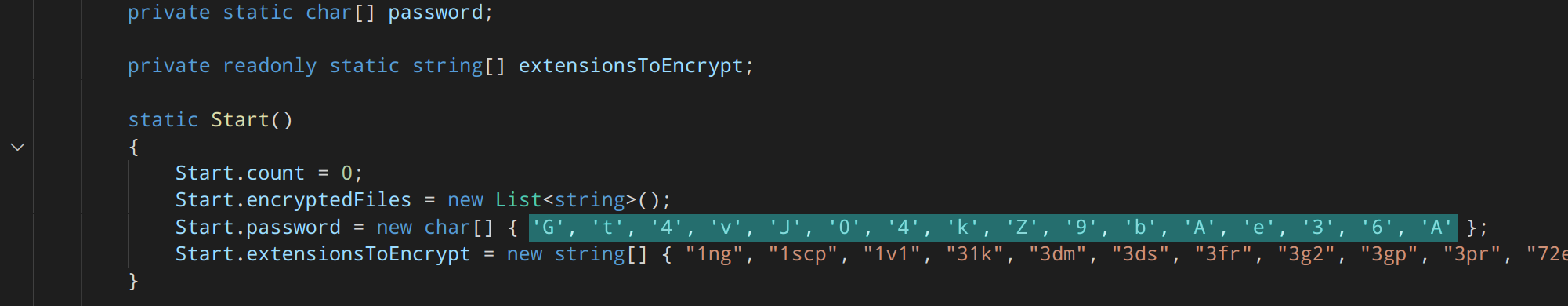
The following file types are targeted for encryption:
"1ng", "1scp", "1v1", "31k", "3dm", "3ds", "3fr", "3g2", "3gp", "3pr", "72e", "7s", "7sp", "7tt", "7z", "ARC", "PAQ", "ab4", "accdb", "accde", "accdr", "accdt", "ach", "acr", "act", "adb", "ads", "aes", "agdl", "ai", "aimi", "ait", "al", "alf", "apj", "apk", "ari", "arw", "asc", "asf", "asm", "asmx", "asp", "aspx", "asset", "asx", "avi", "awg", "back", "backup", "backupdb", "bak", "bank", "bas", "bat", "bay", "bdb", "bgt", "big", "bik", "bikey", "bin", "bkf", "bkp", "blend", "bmp", "bpw", "brd", "bsa", "bz2", "c", "cab", "cad", "capx", "cd", "cdf", "cdr", "cdr3", "cdr4", "cdr5", "cdr6", "cdrw", "cdx", "ce1", "ce2", "cer", "cfm", "cfp", "cgi", "cgm", "cib", "class", "cls", "cmd", "cmt", "cfg", "conf", "config", "cos", "cpi", "cpp", "cr2", "craw", "crt", "crw", "cs", "csh", "csl", "csproj", "csr", "csv", "cxi", "dac", "dat", "db", "db3", "dbf", "dbx", "dc2", "dch", "dcr", "dcs", "ddd", "ddoc", "ddrw", "dds", "ddv", "deb", "der", "des", "design", "dgc", "dif", "difz", "dip", "djvu", "dng", "doc", "docb", "docm", "docx", "dot", "dotm", "dots", "dotx", "drf", "drw", "dtd", "dwg", "dxb", "dxf", "dxg", "edb", "eip", "eml", "epk", "eps", "erbsql", "erf", "exf", "fdb", "ff", "ffd", "fff", "fh", "fhd", "fla", "flac", "flv", "fmb", "forge", "fpx", "frm", "fxg", "g8z", "gblorb", "gif", "go", "gpg", "gpx", "gray", "grey", "gry", "gz", "h", "hbk", "hpp", "htm", "html", "hwp", "ibank", "ibd", "ibz", "idx", "iif", "iiq", "img", "incpas", "indd", "iso", "j6i", "jar", "java", "jpe", "jpeg", "jpg", "js", "json", "jsp", "k25", "kbx", "kc2", "kdbx", "kdc", "key", "kml", "kmz", "kpdx", "lay", "lay6", "lbf", "ldf", "litemod", "log", "ltd", "ltx", "lua", "m", "m2ts", "m3u", "m4a", "m4u", "m4v", "max", "md", "mdb", "mdc", "mdf", "mdl", "mef", "mfw", "mid", "mkv", "mlv", "mml", "mmw", "moneywell", "mos", "mov", "mp3", "mp4", "mpeg", "mpeg4", "mpg", "mpk", "mpq", "mrw", "msg", "myd", "myi", "nd", "ndd", "nef", "nk2", "nop", "nrg", "nrw", "ns2", "ns3", "ns4", "nsd", "nsf", "nsg", "nsh", "nwb", "nx2", "nxl", "nyf", "oab", "obj", "odb", "odc", "odf", "odg", "odm", "odp", "ods", "odt", "ogg", "oil", "old", "onetoc2", "orf", "ost", "otg", "oth", "otp", "ots", "ott", "p12", "p7b", "p7c", "pab", "pages", "pak", "papa", "pas", "pat", "patch", "pbl", "pcd", "pck", "pct", "pdb", "pdd", "pdf", "pef", "pem", "pfx", "php", "php5", "phtml", "pkg", "pl", "plc", "png", "pot", "potm", "pots", "potx", "ppam", "pps", "ppsm", "ppsx", "ppt", "pptm", "pptx", "prf", "ps", "ps1", "psafe3", "psark", "psd", "pspimage", "pst", "psw", "pta", "ptx", "py", "pyc", "qba", "qbb", "qbm", "qbr", "qbw", "qbx", "qby", "qst", "r33", "r3d", "raf", "rar", "rat", "raw", "rb", "rdb", "rem", "rgss3a", "rm", "rofl", "rtf", "rw2", "rwl", "rwz", "rx3", "s3db", "sas7bdat", "sav", "say", "sch", "sd0", "sda", "sdc", "sdd", "sdf", "sdp", "sdw", "sgl", "sh", "sldm", "sldx", "slk", "sln", "snt", "spx1", "sql", "sqlite", "sqlite3", "sqlitedb", "sr2", "srf", "srt", "srw", "st4", "st5", "st6", "st7", "st8", "stc", "std", "sti", "stw", "stx", "suo", "sv2i", "svg", "swf", "swift", "sxc", "sxd", "sxg", "sxi", "sxm", "sxw", "t3", "tar", "targz", "tbk", "tc", "tex", "tga", "tgz", "thm", "tib", "tif", "tiff", "tiger", "tlg", "ttarch", "txt", "uasset", "uax", "unicy3d", "uof", "uop", "uot", "upk", "vb", "vbproj", "vbs", "vcd", "vcf", "vdi", "vef", "vib", "vmdk", "vmx", "vob", "vor", "vsd", "vsdx", "wallet", "war", "wav", "wb2", "wk1", "wkl", "wks", "wma", "wmf", "wmv", "wpd", "wpl", "wps", "wsf", "wtf", "x11", "x3f", "xex", "xhtml", "xis", "xla", "xlam", "xlc", "xlk", "xlm", "xlr", "xls", "xlsb", "xlsm", "xlsx", "xlt", "xltm", "xltx", "xlw", "xml", "xtbl", "ycbcra", "ydk", "yrp", "yuv", "ze4", "zip"
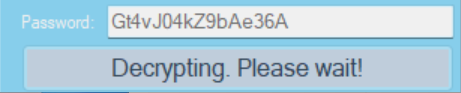
Upon entering the decryption key “Gt4vJ04kZ9bAe36A” into the ransomware interface, all files are decrypted back to their original form:
We reached out to ranzon@protonmail.com but did not receive a reply.
SonicWall Capture Labs provides protection against this threat via the following signature:
- GAV: BitPyLock.RSM (Trojan)
This threat is also detected by SonicWall Capture ATP w/RTDMI and the Capture Client endpoint solutions.