Linux Kernel ksmbd Integer Underflow Vulnerability
Overview:
SonicWall Capture Labs Threat Research Team has observed the following threat:
KSMBD stands for Kernel-based SMB Direct. It’s a Linux kernel module that provides the implementation of the SMBv3 protocol, allowing the Linux kernel to act as a server for SMB (Server Message Block) clients. SMB is a protocol used for sharing files, printers, and other resources between computers in a network.
SMBv3 is the latest version of the protocol and provides several new features and improvements over previous versions, including better security features such as encryption, improved performance, and better support for large files and high-availability scenarios.
KSMBD enables the Linux kernel to directly handle SMB requests, eliminating the need for a user-space daemon to translate the requests into kernel calls. This results in improved performance and lower overhead compared to traditional SMB implementations that rely on user-space daemons.
A denial of service vulnerability has been reported for Linux kernel. This vulnerability is due to an integer underflow in the ksmbd_decode_ntlmssp_auth_blob function.
A remote, unauthenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted request to the target server. Successfully exploiting this vulnerability could result in denial of service.
CVE Reference:
This vulnerability has been assigned the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) identifier CVE-2023-0210.
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS):
The overall CVSS score is 6.7 (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:N/A:H/E:P/RL:O/RC:C).
Base score is 7.5 (AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:N/A:H), based on the following metrics:
• Attack vector is network.
• Attack complexity is low.
• Privileges required is none.
• User interaction is none.
• Scope is unchanged.
• Impact of this vulnerability on data confidentiality is none.
• Impact of this vulnerability on data integrity is none.
• Impact of this vulnerability on data availability is high.
Temporal score is 6.7 (E:P/RL:O/RC:C), based on the following metrics:
• The exploit code maturity level of this vulnerability is proof of concept.
• The remediation level of this vulnerability is official fix.
• The report confidence level of this vulnerability is confirmed.
Technical Overview:
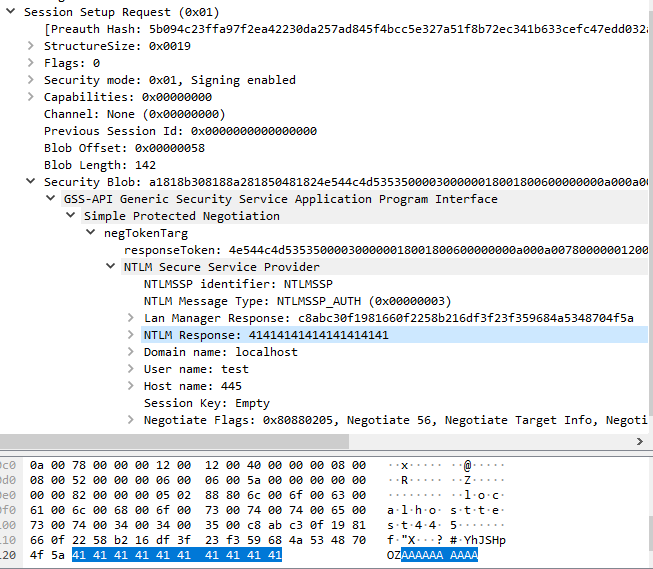
NTLMSSP is a proprietary authentication protocol used in Microsoft Windows. It involves the exchange of a series of messages between the client and the server to establish the authenticity of the client. The messages are encoded using the ASN.1 (Abstract Syntax Notation One) standard and serialized using the DER (Distinguished Encoding Rules) format. Understanding the details of NTLMSSP authentication, as well as the encoding and serialization formats used, is important for understanding this vulnerability.
There is an integer underflow exists in the ksmbd kernel module when handling SMB2 SESSION_SETUP messages. Specifically, the flaw exists due to failure of message validation when processing the NTLMSSP authentication messages. A vulnerable function ksmbd_decode_ntlmssp_auth_blob() is responsible for handling the NTLMSSP_AUTH message. It extracts the value from Length for NTLM Response field and store it into a local variable nt_len. Then, it uses the calculation result of nt_len – CIFS_ENCPWD_SIZE(16) as the argument blen of the function ksmbd_auth_ntlmv2(). The function ksmbd_auth_ntlmv2() allocates a kernel buffer using size of blen+CIFS_CRYPTO_KEY_SIZE(8) and operates two memory copies using the size of CIFS_CRYPTO_KEY_SIZE and blen respectively.
However, the vulnerable function failed to validate if nt_len is smaller than CIFS_ENCPWD_SIZE(16) or not. A positive value under 16 will result in an integer underflow condition. To make the memory allocation success, the value need to be in the range of 8-15. For example, if the nt_len is 12, then blen would be -4 and the memory allocation size is 4, and the later memory copy with sizes of 8 and 0xFFFFFFFC (-4) both result in the memory overflowed.
Triggering the Problem:
• The vulnerable system must be listening on the vulnerable SMB port, and accept incoming connections.
• The attacker must have connectivity to the target system.
• The attacker must know a valid SMB user name on the target system.
Triggering Conditions:
The attacker connects to the target ksmbd server. The vulnerability is triggered when the attacker sends a crafted SMB2 SESSION_SETUP request with crafted Security Blob field.
Attack Delivery:
The following application protocols can be used to deliver an attack that exploits this vulnerability:
• SMB/CIFS
SonicWall’s, (IPS) Intrusion Prevention System, provides protection against this threat:
• IPS: 3510 Linux Kernel ksmbd DoS 1
Remediation Details:
The risks posed by this vulnerability can be mitigated or eliminated by:
• Configure the vulnerable product to allow access to trusted clients only.
• Update to a non-vulnerable version of the product.
• Filter attack traffic using the signature above.
The vendor has released the following commit regarding this vulnerability:
Vendor Advisory