New Phishing Campaign Leverages Fileless PowerShell execution using LNK
SonicWall has recently spotted a new phishing email campaign spreading actively in the last few days. Malicious email, disguised as a legitimate invoice payment or FedEx receipt, delivers a RAR attachment to the targeted users. Upon extraction of the RAR File, user would see a LNK file that looks like a legit document. LNK file then remotely executes a fileless PowerShell script to download an initial payload. This initial payload then brings down multiple payloads, runs shell code and connects to a command and control (C&C) server, which allows the remote attacker access to the compromised computer

Figure 1: Multi stage attack leveraging LNK files
Phishing Email Campaign:
Phishing email is the most popular tactic for tricking users into clicking malicious content It is also determined to be the initial infection vector for most compromises. Attackers trick email recipients into clicking on an attachment or URL in order to infect their computer or steal information. In this phishing campaign, Fedex receipt or Invoice payment receipt has been sent out to targeted victims.
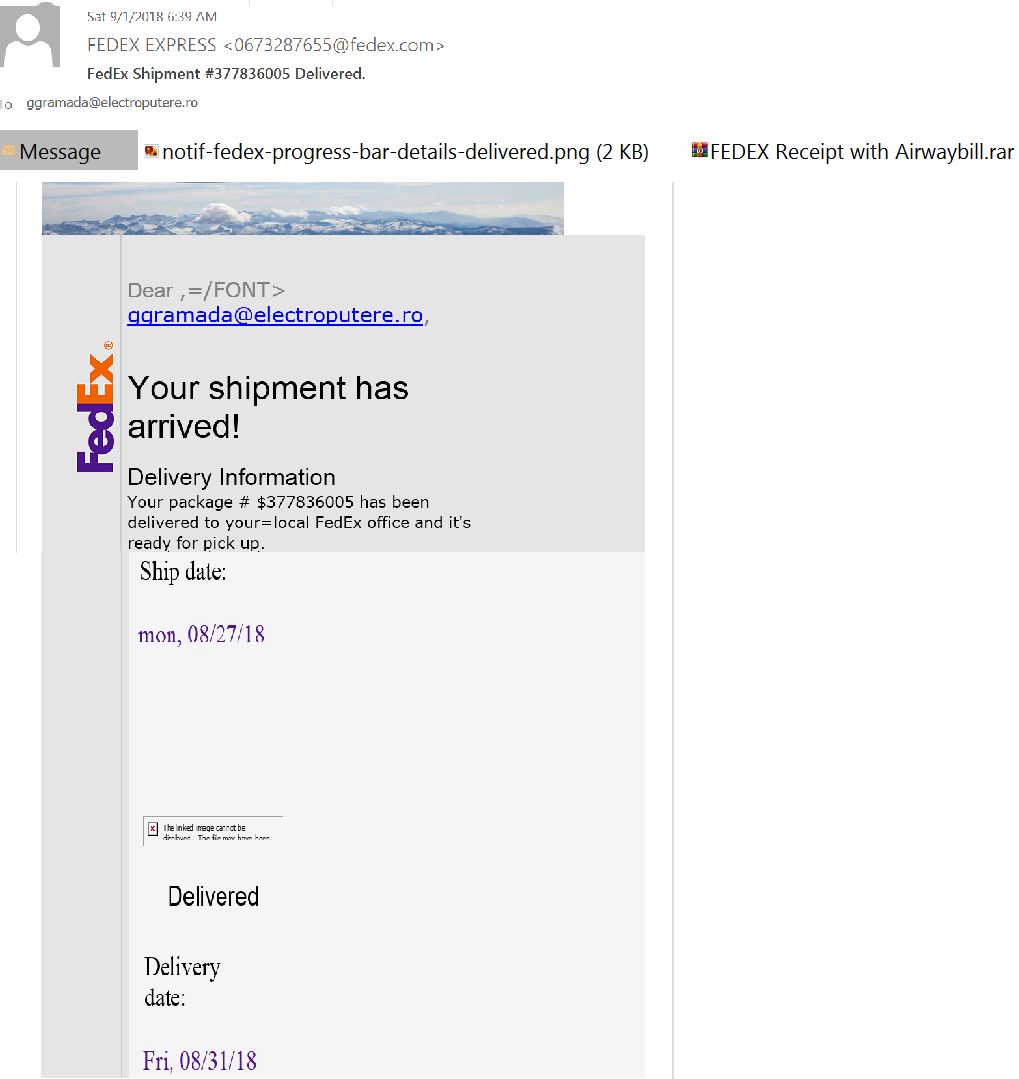
Figure 2: Phishing email used in this campaign
Emails are sent with RAR attachment which when extracted delivers two LNK files.
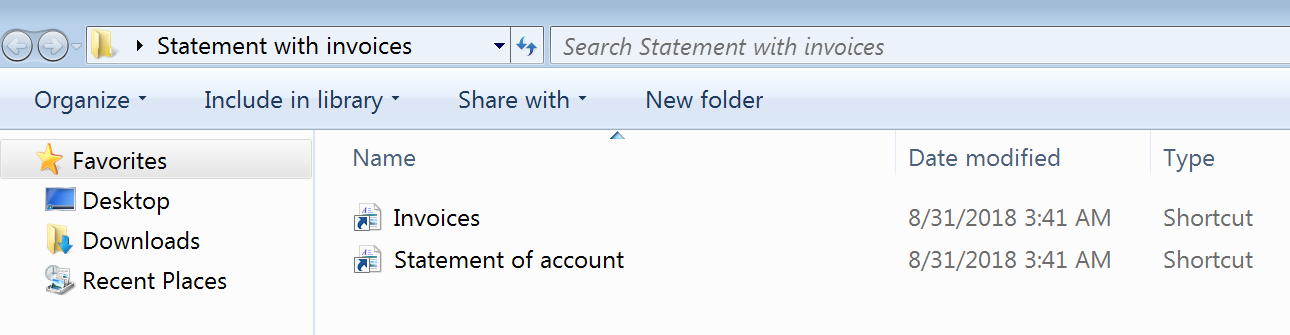
Figure 3: Link files extracted from RAR attachment
LNK file:
LNK is a file extension for a shortcut file used by Microsoft Windows to point to an executable file or an application. LNK files are generally used to create start menu and desktop shortcuts. LNK stands for LiNK.
In this case, LNK files are disguised like a legitimate document by changing the icon using the image resource dll [%SystemRoot%\System32\imageres.dll ] as shown below
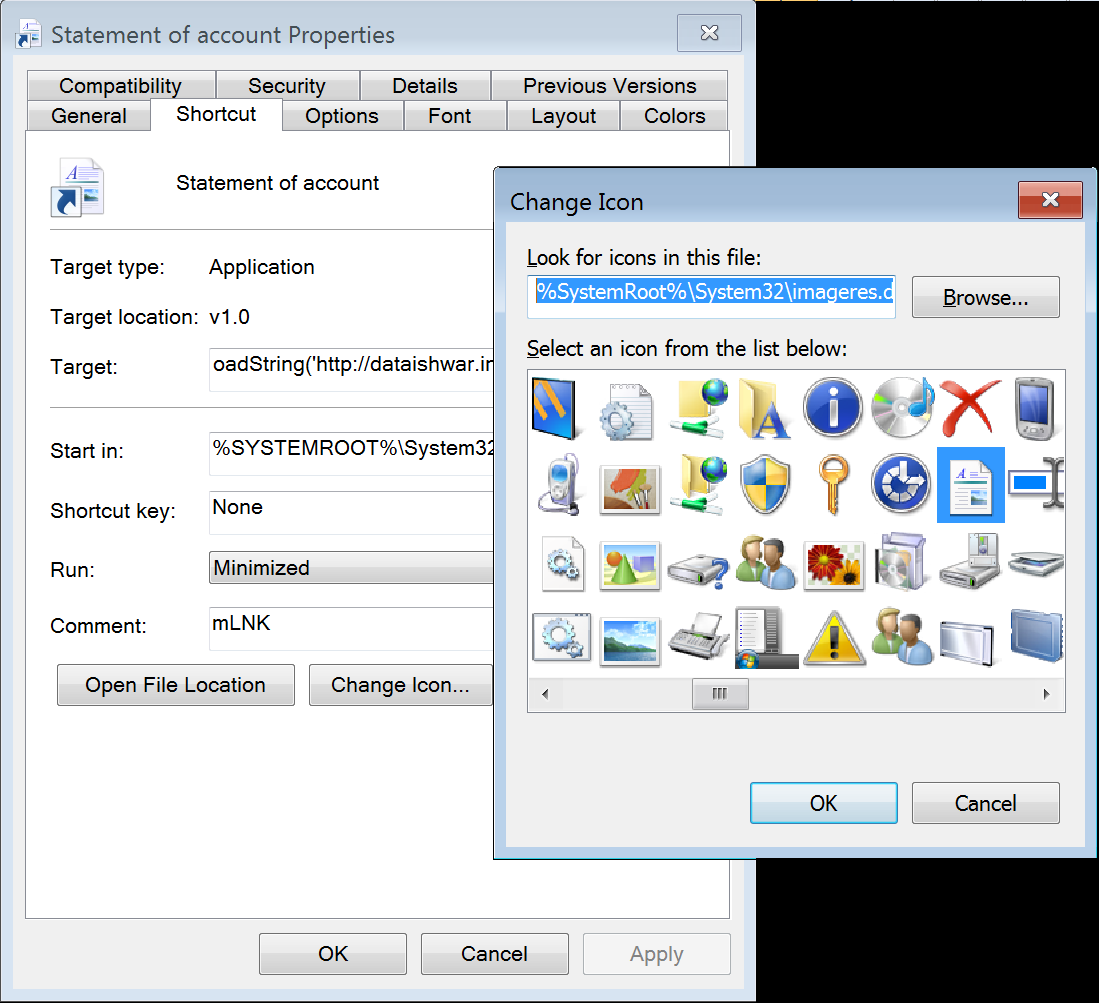
Figure 4: LNK file icon has been modified to look like a legit document
Fileless PowerShell Attack:
In this version, LNK file executes PowerShell.exe.

Figure 6: Fileless PowerShell script execution with IEX
Fileless malware attack occurs by loading malware into memory without writing to disk. Since file never gets into disk, this goes undetected by file based detection. In the above given PowerShell command,
DownloadString method is used to download the content from a remote location (‘http://dataishwar.in/ju/jjl.ps1’) to a buffer $wcli in memory. In this case, even having rules to block execution of certain extension such as .ps1 wouldn’t work as ‘Invoke EXpression (IEX)’ is used.
The IEX Invoke-Expression cmdlet in PowerShell evaluates or runs a specified string as a command and returns the results of the expression.
Malicious PowerShell Script is copied from the remote location and gets executed from memory. It then downloads more malicious payloads to compromise the user machine.
Threat Graph:
Looks like the attacker has hacked into a legitimate site ‘http://dataishwar.in’ & hosted malicious PowerShell scripts and payloads in it. Based on the samples seen date, it must be active since July.
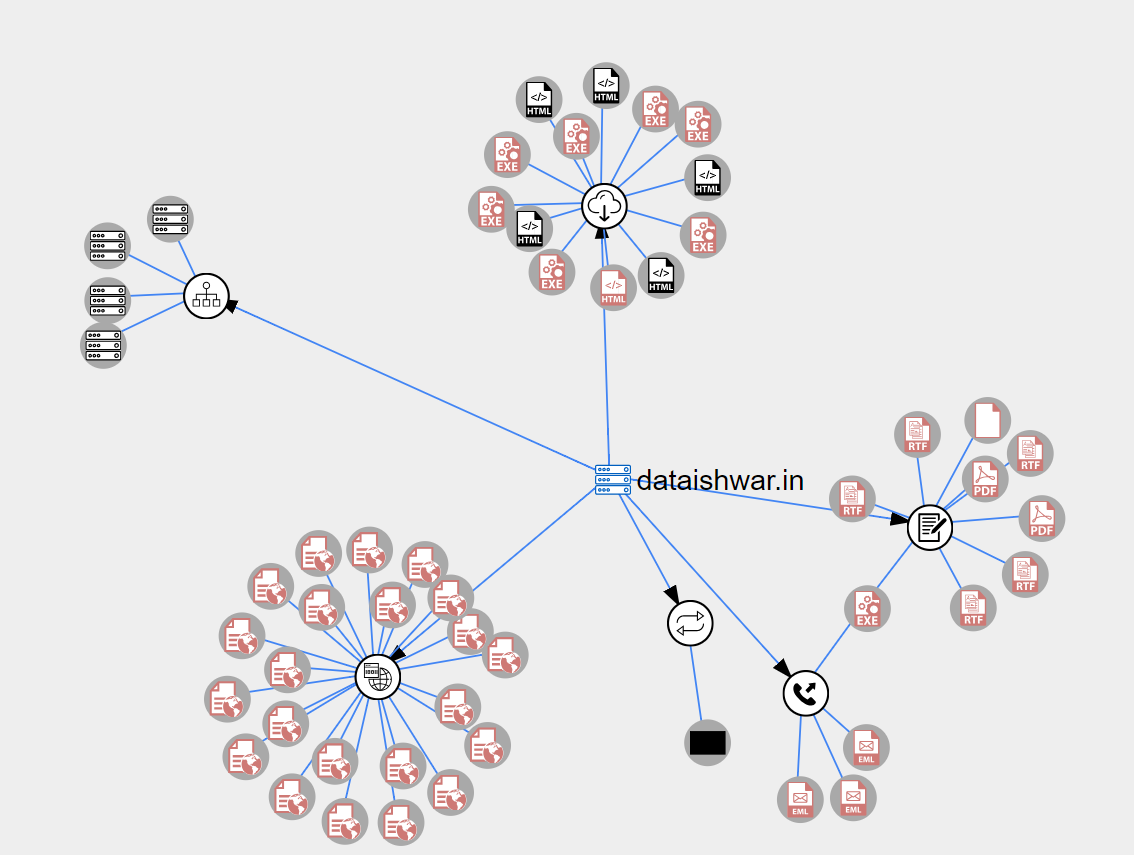
Figure 7: Threat intelligence graph from VirusTotal
Hash:
- 77952875afc68bc3f5aebd99019ea9afda995a17dfb75b6d8de1bd24a70790ff
Listed below are other malicious PowerShell scripts hosted in the same website:
- http://dataishwar.in/mlioc/ortsd.ps
First Seen: 2018-09-04 09:08:43 - http://dataishwar.in/yiu/orrd.ps1
First Seen: 2018-09-02 08:04:18 - http://dataishwar.in/mlioc/ortsd.ps1
First Seen: 2018-09-03 08:46:29 - http://dataishwar.in/cxs/oise.ps1
First Seen: 2018-09-02 10:39:05
Trend Graph:
SonicWall has observed a spike in detection in the last few days.
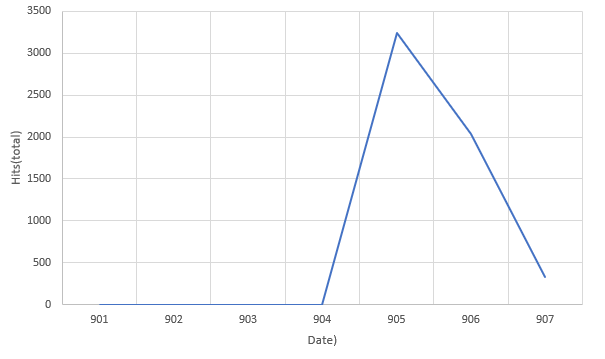
Figure 7: Hits graph
Sonicwall Threat Research Lab provides protection against this exploit with the following signatures:
- GAV 7968: Downloader.FBQH
- IPS 13513: LNK Remote Code Execution (JUN 17) 1
- IPS 13514: LNK Remote Code Execution (JUN 17) 2





